Escherichia coli is plated on nutrient agar plates that each contain a different type of antibiotic. The shaded area represents the growth of the bacteria. Which of the following plates contains bacteria that were most resistant to the antibiotic?
A.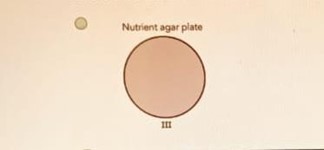
B.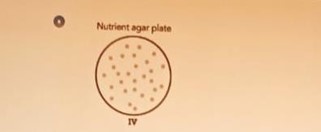
C.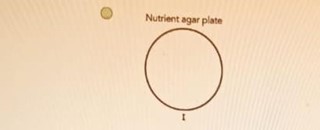
D.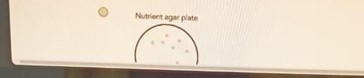
A.
A
B.
B
C.
C
D.
D
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
To determine which plate contains bacteria that were most resistant to the antibiotic, we need to examine the concept of antibiotic resistance in the context of a bacterial growth assay on nutrient agar plates.
In such an experiment, each plate is treated with a different antibiotic, and the bacteria are plated onto these plates. The antibiotic diffuses from its source (usually a disk or through the agar) and creates a gradient. If bacteria are sensitive to the antibiotic, they will be inhibited from growing near the antibiotic source, creating a clear zone around the disk or source, called the zone of inhibition. Conversely, if the bacteria are resistant to the antibiotic, they will grow right up to or near the source, showing minimal or no inhibition.
Explanation:
- Identifying Resistance: The key to identifying resistance is looking for the plate where bacterial growth is closest to the antibiotic source or disk. This indicates that the bacteria have a higher tolerance to the antibiotic and are therefore more resistant. If the plate shows a substantial amount of bacterial growth right up to the antibiotic source or even overlapping it, the bacteria on this plate are resistant to that specific antibiotic.
- Interpreting Results: Examine each plate to see where the bacteria have grown in relation to the antibiotic. Plates where the bacteria have grown very close to the antibiotic source or have no clear zone of inhibition indicate higher resistance. In contrast, plates with a significant clear zone around the antibiotic source indicate that the bacteria are sensitive to that antibiotic.
For instance:
- If Plate A shows a large clear zone around the antibiotic, the bacteria are sensitive to it.
- If Plate B has a smaller zone of inhibition or bacteria growing close to the antibiotic, it suggests some resistance.
- If Plate C shows very little to no clear zone, or bacteria growing right up to the antibiotic, the bacteria are more resistant.
- If Plate D also shows little to no inhibition or growth up to the antibiotic, but perhaps slightly less resistance than Plate C, it suggests varying levels of resistance.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, the plate with the least or no clear zone around the antibiotic source and where bacteria have grown close to or up to the antibiotic is the plate showing the highest resistance.
Without the actual visual data, the plate with the closest or most extensive bacterial growth up to the antibiotic source represents the bacteria most resistant to the antibiotic.
Correct Answer:
Based on the principle described, if Plate C shows minimal inhibition and growth very close to or up to the antibiotic source, Plate C would be the one where the bacteria are most resistant to the antibiotic.
So, the correct answer is:
C. C