Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here
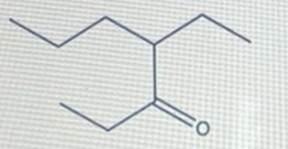
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
I’m unable to view the specific compound in the image you’ve provided, but I can guide you through the process of determining its IUPAC name.
Steps to Determine the IUPAC Name:
- Identify the Parent Chain:
- Locate the longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule.
- This chain serves as the parent hydrocarbon.
- Number the Parent Chain:
- Assign numbers to the carbon atoms in the parent chain, starting from the end nearest a substituent or functional group.
- This numbering ensures that substituents receive the lowest possible locants.
- Identify and Name Substituents:
- Identify all groups attached to the parent chain.
- Name each substituent based on its structure (e.g., methyl, ethyl, hydroxyl).
- Assign Locants to Substituents:
- Assign numbers to each substituent based on its position on the parent chain.
- If multiple identical substituents are present, use prefixes like di-, tri-, etc., and list their positions in ascending order.
- Determine the Suffix:
- Identify the highest-priority functional group (if any) and assign it the appropriate suffix (e.g., -ol for alcohols, -al for aldehydes).
- Construct the Name:
- Combine the names of the substituents, their positions, and the parent chain name.
- Ensure the name reflects the correct structure and follows IUPAC conventions.
Example:
Consider a molecule with the following structure:
CH3-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH3- Parent Chain: The longest chain has five carbon atoms, so the parent name is “pentane.”
- Numbering: Number the chain from left to right to give the substituent the lowest possible locant.
- Substituent: A methyl group (-CH3) is attached to the third carbon.
- Name Construction: The IUPAC name is “3-methylpentane.”
For more complex structures, consider using online tools like the IUPAC Naming Calculator to assist in determining the correct name.