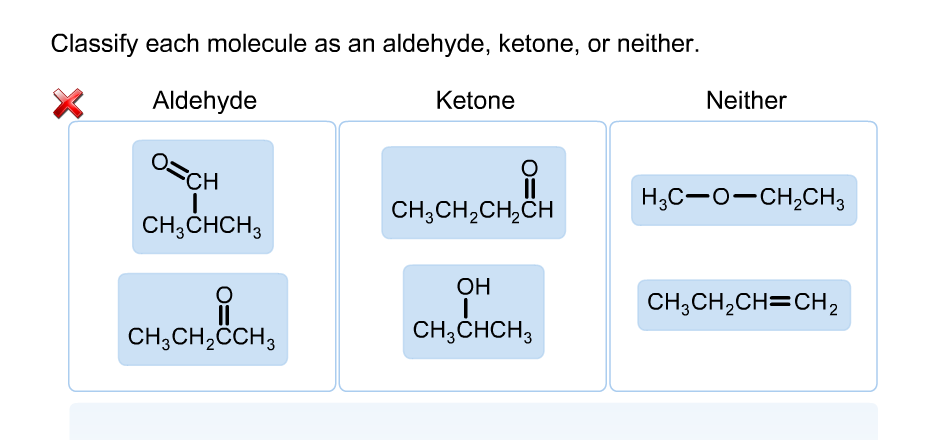
Classify each molecule as an aldehyde, ketone, or neither
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O). The key distinction between them lies in the bonding of the carbonyl carbon:
- Aldehydes: The carbonyl carbon is bonded to at least one hydrogen atom and may also be bonded to another carbon atom or a hydrogen atom. This structure gives aldehydes the general formula R-CHO, where R represents a hydrocarbon group. Aldehydes are typically found at the end of carbon chains. citeturn0search1
- Ketones: The carbonyl carbon is bonded to two hydrocarbon groups, which can be either alkyl groups or aryl groups. Ketones have the general formula R-CO-R’, where R and R’ are hydrocarbon groups. The carbonyl group in ketones is usually located within the carbon chain. citeturn0search1
To classify molecules as aldehydes, ketones, or neither, examine the structure of each molecule:
- Identify the Carbonyl Group: Look for a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O).
- Determine the Bonding of the Carbonyl Carbon:
- If the carbonyl carbon is bonded to at least one hydrogen atom, the molecule is an aldehyde.
- If the carbonyl carbon is bonded to two hydrocarbon groups, the molecule is a ketone.
- Check for Other Functional Groups: If the molecule contains functional groups other than the carbonyl group, it may be classified as neither an aldehyde nor a ketone.
For example, consider the molecule CH₃CHO:
- The structure shows a carbonyl group (C=O) with a hydrogen atom and a methyl group (CH₃) attached to the carbonyl carbon.
- Since the carbonyl carbon is bonded to a hydrogen atom, this molecule is an aldehyde.
In contrast, a molecule like CH₃COCH₃ has a carbonyl group bonded to two methyl groups.
- Here, the carbonyl carbon is bonded to two hydrocarbon groups, classifying the molecule as a ketone.
Understanding these structural distinctions is crucial for accurately classifying organic compounds as aldehydes, ketones, or neither.