Design a combinational circuit that generates the 9’s complement of a
(a) BCD digit. (HDL—see Problem 4.54(a))
(b) Gray-code digit. (HDL—see Problem 4.54(b))
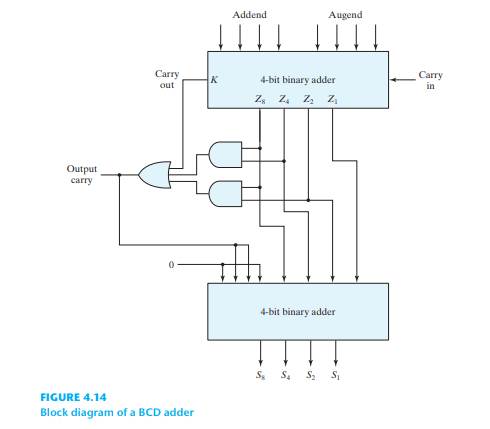
Construct a BCD adder D-subtractor circuit. Use the BCD adder of Fig. 4.14 and the 9’s complementer of Problem 4.18. Use block diagrams for the components. (HDL—see Problem 4.55)
Problem 4.54
Develop and simulate a HDL behavioral model of a circuit that generates the 9’s complement of
(a) a BCD digit (see Problem 4.18(a)).
(b) a Gray-code digit (see Problem 4.18(b).)
Problem 4.18
Design a combinational circuit that generates the 9’s complement of a
(a) BCD digit. (HDL—see Problem 4.54(a))
(b) Gray-code digit. (HDL—see Problem 4.54(b))
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
To solve the problem of designing a combinational circuit that generates the 9’s complement for both BCD (Binary Coded Decimal) and Gray-code digits, we will approach each part systematically.
(a) 9’s Complement of a BCD Digit
A BCD digit represents a decimal number (0-9) using four bits. To generate the 9’s complement of a BCD digit, we subtract the BCD value from 9. The 9’s complement of a decimal number is simply 9 minus the given digit. This can be done by inverting the bits of the BCD digit and adding 1.
Steps:
- Inversion: The 9’s complement of a BCD digit is achieved by taking the binary representation and flipping each bit.
- Addition of 1: After inverting the bits, you add a binary 1 to the result.
For example, if the input is 0001 (BCD for decimal 1), the inverted value is 1110. Adding 1 gives 1111, which is the 9’s complement of 1 (decimal 8).
HDL Code for BCD 9’s Complementer:
module bcd_complement(input [3:0] bcd, output [3:0] complement);
assign complement = 9 - bcd;
endmodule(b) 9’s Complement of a Gray-code Digit
Gray-code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit. To generate the 9’s complement of a Gray-code digit, the process is similar to the BCD complement but needs to account for the Gray-code representation.
Steps:
- Convert the Gray-code digit to its corresponding binary value.
- Compute the 9’s complement by subtracting the binary value from 9.
- Convert the result back to Gray-code.
The conversion from Gray-code to binary involves applying XOR operations.
HDL Code for Gray-code 9’s Complementer:
module gray_complement(input [3:0] gray, output [3:0] complement);
reg [3:0] binary;
// Convert Gray-code to Binary
always @ (gray) begin
binary[3] = gray[3];
binary[2] = binary[3] ^ gray[2];
binary[1] = binary[2] ^ gray[1];
binary[0] = binary[1] ^ gray[0];
end
// 9's complement of the binary value
assign complement = 9 - binary;
endmoduleBCD Adder and Subtractor
To design a BCD adder/subtractor circuit using the above components, we first need to use a BCD adder like the one shown in Figure 4.14 (the actual figure is not included here, but it typically consists of a 4-bit adder with extra logic to handle carry generation). The BCD adder can be used in conjunction with the 9’s complementer to handle subtraction.
Block Diagram of BCD Adder-Subtractor
- BCD Adder: The BCD adder adds two BCD digits, with special logic to handle carry and adjust for the fact that a BCD result cannot exceed 9.
- 9’s Complementer: For subtraction, the second operand is complemented using the 9’s complementer and then added to the first operand.
HDL Behavioral Model for BCD Adder-Subtractor
module bcd_adder_subtractor(input [3:0] bcd1, bcd2, input subtract, output [3:0] result, output carry);
wire [3:0] bcd2_complement;
// Generate 9's complement if subtract is 1
bcd_complement complementer(bcd2, bcd2_complement);
// Add or subtract based on the 'subtract' signal
wire [3:0] operand2 = (subtract) ? bcd2_complement : bcd2;
wire [4:0] sum = bcd1 + operand2 + subtract;
// If sum > 9, adjust for BCD
assign result = (sum > 9) ? sum - 10 : sum;
assign carry = (sum > 9);
endmoduleExplanation
- The BCD adder-subtractor combines a BCD adder and a 9’s complementer for subtraction. The 9’s complement of the second operand is calculated when the subtract flag is set. The addition operation is performed with the adjusted value, and if the sum exceeds 9, a correction is applied to bring it back within the valid range of BCD digits (0-9).
- This method effectively handles both addition and subtraction of BCD digits, using the complement technique for subtraction, which is standard practice in digital arithmetic circuits.