Mensa IQ Scores Picture the Scenario Mensa 6 is a society of high-IQ people whose members have IQ scores at the 98th percentile or higher. The Stanford-Binet IQ scores that are used as the basis for admission into Mensa are approximately normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 16. Questions to Explore a. How many standard deviations above the mean is the 98th percentile? b. What is the IQ score for that percentile? Think It Through a. For a value to represent the 98th percentile, its cumulative probability must equal 0.98, by the definition of a percentile. See Figure 6.9 .
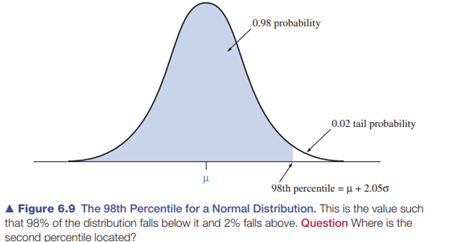
The cumulative probability of 0.980 in the body of Table A corresponds to z = 2.05. The 98th percentile is 2.05 standard deviations above the mean, at μ + 2.05σ. b. Since μ = 100 and σ = 16, the 98th percentile of IQ scores equals μ + 2.05σ = 100 + 2.05(16) = 133. In summary, 98% of the IQ scores fall below 133, and an IQ score of at least 133 is required to join Mensa. Insight About 2% of IQ scores are higher than 133. By symmetry, about 2% of IQ scores are lower than μ – 2.05σ = 100 – 2.05(16) = 67. This is the second percentile. The remaining 96% of the IQ scores fall between 67 and 133, which is the region within 2.05 standard deviations of the mean. It’s also possible to use software to find normal probabilities or z -scores. The margin shows a screen shot using the TI@83+/84 to find the 98th percentile of IQ.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Correct Answer
a. The 98th percentile is 2.05 standard deviations above the mean.
b. The IQ score corresponding to the 98th percentile is calculated as:
[
\text{IQ score} = \mu + z\sigma = 100 + 2.05(16) = 133
]
Explanation (300 words)
The IQ scores used for Mensa admissions follow a normal distribution, a bell-shaped curve described by two parameters: the mean ((\mu)) and the standard deviation ((\sigma)). In this case, the mean is (\mu = 100) and the standard deviation is (\sigma = 16). A percentile represents the percentage of data values below a certain score in the distribution. The 98th percentile signifies that 98% of the IQ scores are below this value.
To determine how many standard deviations above the mean correspond to the 98th percentile, we use the z-score. The z-score indicates the number of standard deviations a value lies from the mean. Using a standard normal distribution table (or software), we find the z-score associated with a cumulative probability of 0.98 is (z = 2.05). This tells us the 98th percentile is 2.05 standard deviations above the mean.
Next, we calculate the corresponding IQ score. Using the formula for a z-score:
[
z = \frac{X – \mu}{\sigma}
]
Rearranging to solve for (X), the IQ score, gives:
[
X = \mu + z\sigma
]
Substituting the known values:
[
X = 100 + 2.05(16) = 133
]
Thus, an IQ score of 133 is the cutoff for the 98th percentile and Mensa eligibility.
Finally, approximately 2% of IQ scores exceed 133, while another 2% fall below (100 – 2.05(16) = 67), the second percentile. The remaining 96% of scores lie between 67 and 133, forming the central range within 2.05 standard deviations of the mean. Software tools like the TI-83/84 can simplify these calculations by directly outputting z-scores or probabilities.