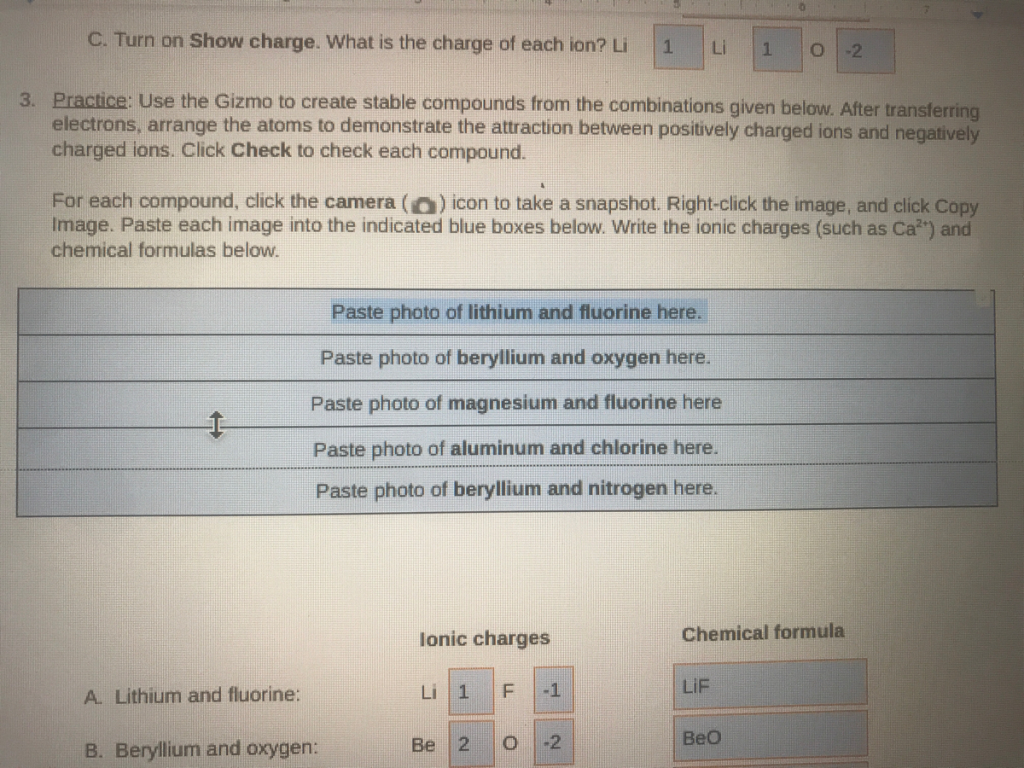
Use the Gizmo to create stable compounds from the combinations given below. After transferring electrons, arrange the atoms to demonstrate the attraction between positively charged ions and negatively charged ions. Click Check to check each compound. For each compound, click the camera () icon to take a snapshot. Right-click the image, and click Copy Image. Paste each image into the indicated blue boxes below. Write the ionic charges (such as Ca²”) and chemical formulas below. B. Beryllium and oxygen: Paste photo of lithium and fluorine here. Paste photo of beryllium and oxygen here. Paste photo of magnesium and fluorine here Paste photo of aluminum and chlorine here. Paste photo of beryllium and nitrogen here. Ionic charges Li 1 Be 2 F LL 1 0 L Li 1 -2 0 -2 LIF Chemical formula BeO
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
To form stable ionic compounds, atoms transfer electrons to achieve full outer electron shells, resulting in positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. Below are the combinations provided, along with their ionic charges and chemical formulas:
- Lithium and Fluorine:
- Ionic Charges: Lithium (Li) loses one electron to form a cation with a +1 charge (Li⁺). Fluorine (F) gains one electron to form an anion with a -1 charge (F⁻).
- Chemical Formula: Li⁺ and F⁻ combine in a 1:1 ratio to form lithium fluoride (LiF).
- Beryllium and Oxygen:
- Ionic Charges: Beryllium (Be) loses two electrons to form a cation with a +2 charge (Be²⁺). Oxygen (O) gains two electrons to form an anion with a -2 charge (O²⁻).
- Chemical Formula: Be²⁺ and O²⁻ combine in a 1:1 ratio to form beryllium oxide (BeO).
- Magnesium and Fluorine:
- Ionic Charges: Magnesium (Mg) loses two electrons to form a cation with a +2 charge (Mg²⁺). Fluorine (F) gains one electron to form an anion with a -1 charge (F⁻).
- Chemical Formula: To balance the charges, two fluoride ions are needed for each magnesium ion, resulting in magnesium fluoride (MgF₂).
- Aluminum and Chlorine:
- Ionic Charges: Aluminum (Al) loses three electrons to form a cation with a +3 charge (Al³⁺). Chlorine (Cl) gains one electron to form an anion with a -1 charge (Cl⁻).
- Chemical Formula: To balance the charges, three chloride ions are needed for each aluminum ion, resulting in aluminum chloride (AlCl₃).
- Beryllium and Nitrogen:
- Ionic Charges: Beryllium (Be) loses two electrons to form a cation with a +2 charge (Be²⁺). Nitrogen (N) gains three electrons to form an anion with a -3 charge (N³⁻).
- Chemical Formula: To balance the charges, three beryllium ions are needed for every two nitrogen ions, resulting in beryllium nitride (Be₃N₂).
These compounds are formed through the transfer of electrons, leading to the formation of ions that are held together by strong electrostatic forces in a lattice structure. The resulting compounds are electrically neutral, with the total positive charge equal to the total negative charge.
For a visual representation of these ionic compounds, you can use the Ionic Bonds Gizmo to simulate the electron transfer and observe the formation of these compounds.
Note: The provided image link appears to be broken or inaccessible. Please use the Gizmo link above to access the simulation.