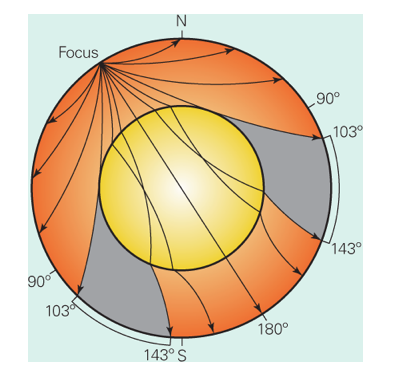
What are P-wave and S-wave shadow zones, and what do they tell us? Which type does the figure show?
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
P-waves (Primary waves) and S-waves (Secondary waves) are two primary types of seismic waves generated by earthquakes. P-waves are compressional waves that move through both solids and liquids, while S-waves are shear waves that can only travel through solids. The regions where these waves are not detected are known as shadow zones.
P-Wave Shadow Zone:
P-waves can travel through both solids and liquids. However, when they encounter the Earth’s liquid outer core, they are refracted due to the change in material properties. This refraction causes a P-wave shadow zone on the Earth’s surface, typically between 104° and 140° from the earthquake’s epicenter. Within this angular range, seismographs do not detect direct P-waves because they are refracted away from the Earth’s surface.
S-Wave Shadow Zone:
S-waves cannot travel through liquids. When they encounter the Earth’s liquid outer core, they are completely absorbed, creating an S-wave shadow zone. This shadow zone is typically observed beyond 104° from the earthquake’s epicenter, as S-waves are not detected in this region due to their inability to pass through the liquid outer core.
Significance of Shadow Zones:
The existence of P-wave and S-wave shadow zones provides critical information about the Earth’s internal structure:
- Core Composition: The S-wave shadow zone indicates the presence of a liquid outer core, as S-waves cannot travel through liquids. The P-wave shadow zone, combined with the S-wave shadow zone, suggests that the outer core is liquid, while the inner core is solid.
- Earth’s Interior Structure: By analyzing the size and extent of these shadow zones, scientists can infer the size and composition of the Earth’s core, mantle, and crust, leading to a better understanding of the planet’s internal dynamics.
Regarding the figure you provided, without direct access to the image, I cannot definitively identify which type of shadow zone it depicts. However, if the figure shows a region where seismic waves are absent due to refraction and absorption by the Earth’s core, it is likely illustrating the P-wave and S-wave shadow zones.
In summary, P-wave and S-wave shadow zones are essential for understanding the Earth’s internal composition and structure. They reveal the presence of a liquid outer core and provide insights into the behavior of seismic waves as they traverse different layers of the Earth.