Which is a correct Lewis structure for carbonic acid, H2CO3?
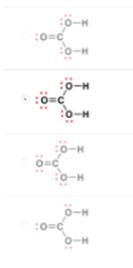
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The correct Lewis structure for carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) features a central carbon atom double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to two hydroxyl groups (–OH). Each oxygen atom in the hydroxyl groups carries two lone pairs of electrons, while the oxygen double-bonded to carbon has two lone pairs. This arrangement satisfies the octet rule for all atoms involved.
Steps to Draw the Lewis Structure:
- Determine Total Valence Electrons:
- Hydrogen (H): 1 electron × 2 = 2 electrons
- Carbon (C): 4 electrons
- Oxygen (O): 6 electrons × 3 = 18 electrons
- Total valence electrons = 2 + 4 + 18 = 24 electrons
- Identify the Central Atom:
- Carbon is less electronegative than oxygen and can form four bonds, making it the central atom.
- Sketch the Skeleton Structure:
- Place carbon at the center, bonded to two hydroxyl groups and double-bonded to one oxygen atom.
- Distribute Electrons as Bonds:
- Each single bond (C–O) uses 2 electrons, and the double bond (C=O) uses 4 electrons.
- Total electrons used in bonds = 2 × 2 (for two single bonds) + 4 (for the double bond) = 8 electrons.
- Assign Lone Pairs to Oxygen Atoms:
- Each oxygen atom needs 8 electrons to complete its octet.
- The oxygen double-bonded to carbon has two lone pairs.
- Each oxygen in the hydroxyl groups has two lone pairs.
- Verify the Octet Rule:
- All atoms (carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen) satisfy the octet rule, with hydrogen achieving a duet.
Formal Charge Calculation:
- Formal charge = Valence electrons – (Nonbonding electrons + ½ Bonding electrons)
For each atom:
- Hydrogen: 1 – (0 + ½ × 2) = 0
- Carbon: 4 – (0 + ½ × 8) = 0
- Oxygen (double-bonded to carbon): 6 – (4 + ½ × 4) = 0
- Oxygen (single-bonded to carbon and hydrogen): 6 – (4 + ½ × 4) = 0
All atoms have a formal charge of zero, indicating a stable structure.
Molecular Geometry:
- The central carbon atom is sp² hybridized, leading to a trigonal planar geometry with bond angles of approximately 120°.
Polarity:
- The molecule is polar due to the presence of polar O–H bonds and the asymmetrical arrangement of atoms.
This Lewis structure accurately represents the bonding and electron distribution in carbonic acid, adhering to the octet rule and minimizing formal charges.