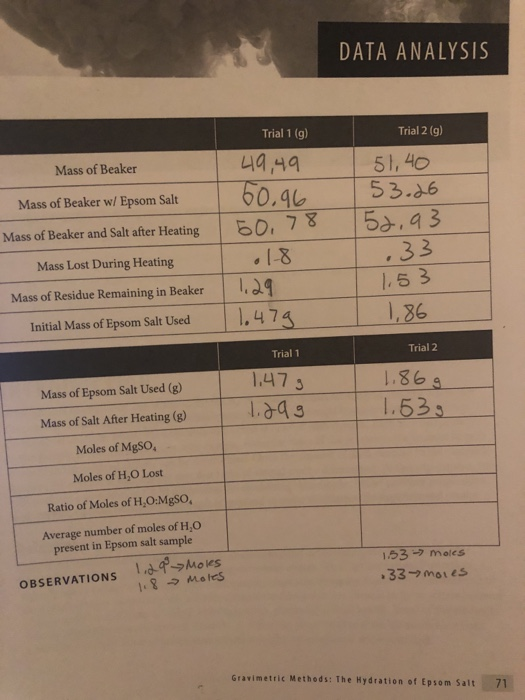
how do i convert grams to moles? and what is the ratio?
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Converting grams to moles is a fundamental process in chemistry that allows you to determine the amount of a substance in terms of the number of particles it contains. This conversion is essential for stoichiometric calculations, which are used to predict the quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
Understanding Moles and Grams
A mole is a unit in chemistry that represents a specific quantity of particles, such as atoms or molecules. One mole contains approximately (6.022 \times 10^{23}) particles, a number known as Avogadro’s number. The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance, typically expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). For example, the molar mass of water (H₂O) is approximately 18.015 g/mol, meaning one mole of water weighs 18.015 grams.
Conversion Formula
To convert grams to moles, you can use the following formula:
[ \text{Moles} = \frac{\text{Mass (grams)}}{\text{Molar Mass (g/mol)}} ]
Steps to Convert Grams to Moles
- Determine the Molar Mass: Find the molar mass of the substance by summing the atomic masses of all elements in its chemical formula. Atomic masses can be found on the periodic table.
- Apply the Conversion Formula: Divide the mass of the substance (in grams) by its molar mass (in g/mol) to calculate the number of moles.
Example Calculation
Suppose you have 50 grams of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and want to find the number of moles:
- Calculate the Molar Mass of CO₂:
- Carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
- Molar Mass of CO₂ = 12.01 g/mol + (2 × 16.00 g/mol) = 44.01 g/mol
- Convert Grams to Moles:
- Moles of CO₂ = 50 g ÷ 44.01 g/mol ≈ 1.136 moles
Therefore, 50 grams of CO₂ is approximately 1.136 moles.
Importance of Conversion
Converting grams to moles is crucial for:
- Stoichiometric Calculations: Determining the proportions of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
- Solution Preparation: Calculating the amount of solute needed to prepare solutions of desired concentrations.
- Chemical Analysis: Quantifying substances in laboratory experiments.
By mastering this conversion, you can accurately perform a wide range of chemical calculations and analyses.