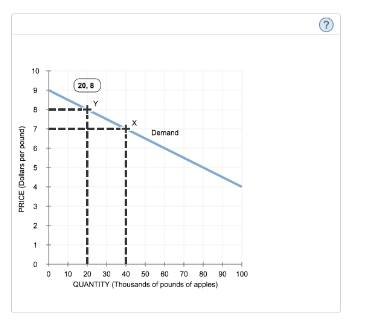
According to the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand for apples between point X and point Y is approximately, which suggests that the demand for apples is between points X and Y.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The midpoint method, also known as the arc elasticity method, is a technique used to calculate the price elasticity of demand (PED) between two points on a demand curve. This method addresses the issue of differing elasticity values when calculating percentage changes using initial or final values as bases. By using the average (midpoint) of the initial and final values, the midpoint method provides a consistent measure of elasticity regardless of the direction of the price change.
Formula for the Midpoint Method:
The price elasticity of demand between two points (X and Y) is calculated using the following formula:
[ \text{PED} = \frac{\left( \frac{Q_Y – Q_X}{(Q_Y + Q_X)/2} \right)}{\left( \frac{P_Y – P_X}{(P_Y + P_X)/2} \right)} ]
Where:
- ( P_X ) and ( P_Y ) are the initial and final prices, respectively.
- ( Q_X ) and ( Q_Y ) are the initial and final quantities demanded, respectively.
Steps to Calculate PED Using the Midpoint Method:
- Calculate the Average Price and Quantity:
- Average Price = ( \frac{P_X + P_Y}{2} )
- Average Quantity = ( \frac{Q_X + Q_Y}{2} )
- Determine the Percentage Changes:
- Percentage Change in Quantity = ( \frac{Q_Y – Q_X}{\text{Average Quantity}} \times 100 )
- Percentage Change in Price = ( \frac{P_Y – P_X}{\text{Average Price}} \times 100 )
- Compute the Price Elasticity of Demand:
- PED = ( \frac{\text{Percentage Change in Quantity}}{\text{Percentage Change in Price}} )
Example Calculation:
Suppose the price of apples increases from $2 to $3, and the quantity demanded decreases from 100 units to 80 units.
- Calculate the Average Price and Quantity:
- Average Price = ( \frac{2 + 3}{2} = 2.5 )
- Average Quantity = ( \frac{100 + 80}{2} = 90 )
- Determine the Percentage Changes:
- Percentage Change in Quantity = ( \frac{80 – 100}{90} \times 100 = -22.22\% )
- Percentage Change in Price = ( \frac{3 – 2}{2.5} \times 100 = 40\% )
- Compute the Price Elasticity of Demand:
- PED = ( \frac{-22.22\%}{40\%} = -0.56 )
The negative sign indicates an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, as expected. The magnitude of 0.56 suggests that the demand for apples is inelastic between points X and Y, meaning that the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price. In other words, consumers are relatively unresponsive to price changes in this range.
Interpretation of PED Values:
- Elastic Demand (PED > 1): Consumers are highly responsive to price changes; a small change in price leads to a large change in quantity demanded.
- Unitary Elastic Demand (PED = 1): The percentage change in quantity demanded equals the percentage change in price.
- Inelastic Demand (PED < 1): Consumers are less responsive to price changes; a large change in price leads to a small change in quantity demanded.
In this example, with a PED of 0.56, the demand for apples is inelastic between points X and Y. This means that a 1% increase in price would result in a 0.56% decrease in quantity demanded. Understanding the elasticity of demand is crucial for businesses and policymakers, as it helps predict how changes in price will affect total revenue and consumer behavior.
For a more detailed explanation and additional examples, you can refer to Quickonomics’ guide on calculating price elasticities using the midpoint formula.