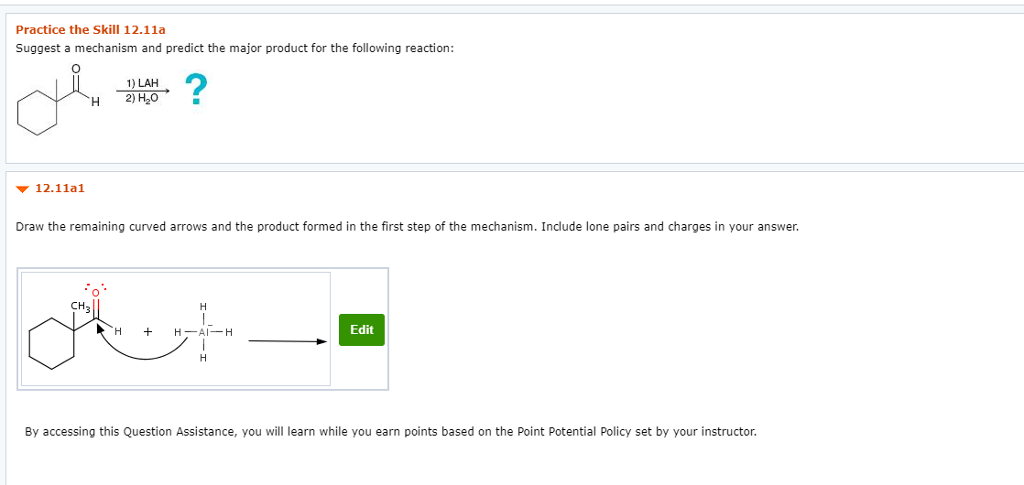
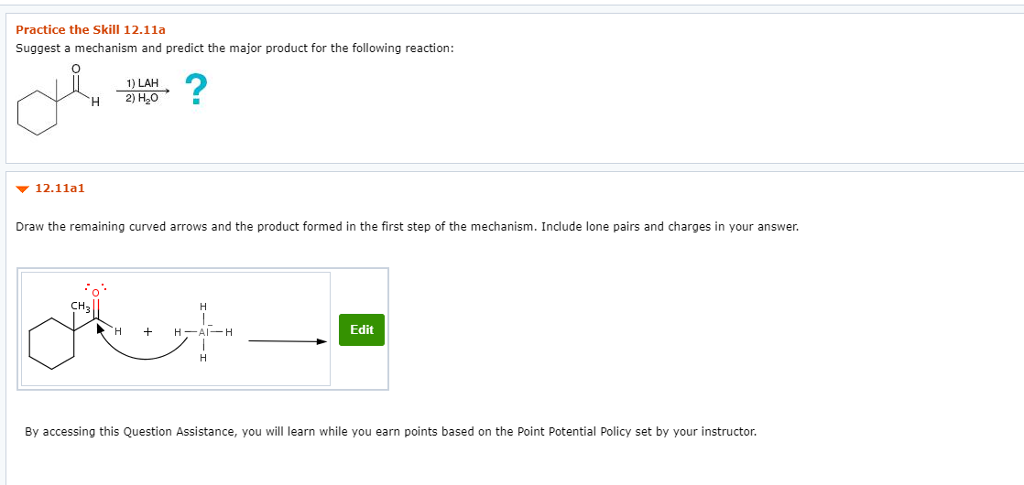
Suggest a mechanism and predict the major product for the following reaction: Draw the remaining curved arrows and the product formed in the first step of the mechanism. Include lone pairs and charges in your answer. By accessing this Question Assistance, you will learn while you earn points based on the Point Potential Policy set by your instructor.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The specific question and diagram linked cannot be directly accessed. However, I can provide guidance on solving this type of reaction mechanism question. Please describe the reaction or include any relevant chemical structure details, and I’ll help draft a complete solution. If it involves standard mechanisms like nucleophilic substitution, elimination, or electrophilic addition, here’s how to approach it:
Steps to Determine the Mechanism and Predict the Major Product:
- Analyze the Reactants:
- Identify the functional groups present.
- Look for reactive sites such as electrophilic carbons (e.g., carbons bonded to halogens or oxygen) or nucleophilic atoms (e.g., atoms with lone pairs or negative charges).
- Reaction Conditions:
- Acidic or basic conditions? This determines the role of catalysts like H⁺ or OH⁻.
- Solvent (polar protic, polar aprotic, etc.), which can influence SN1 vs. SN2 mechanisms.
- Choose the Likely Mechanism:
- SN1: Two steps involving carbocation formation. Often occurs with tertiary substrates and polar protic solvents.
- SN2: Single concerted step. Favored by primary or secondary substrates and polar aprotic solvents.
- E1: Two steps with carbocation formation, leading to elimination.
- E2: Single-step elimination with anti-periplanar geometry.
- Electrophilic Addition: Often occurs in alkenes/alkynes reacting with halogens or acids.
- Predict the Product:
- Follow regioselectivity (Markovnikov or anti-Markovnikov) and stereoselectivity if applicable.
- For elimination, predict Zaitsev’s (more substituted alkene) or Hofmann’s product (less substituted alkene).
- Draw Curved Arrows and Include Charges:
- Show electron movement: from a nucleophile’s lone pair to an electrophile, or from a bond being broken to an atom.
- Include charges, lone pairs, and resonance forms.
If you provide a brief description of the reactants or reaction type, I can write out the detailed mechanism and explanation!