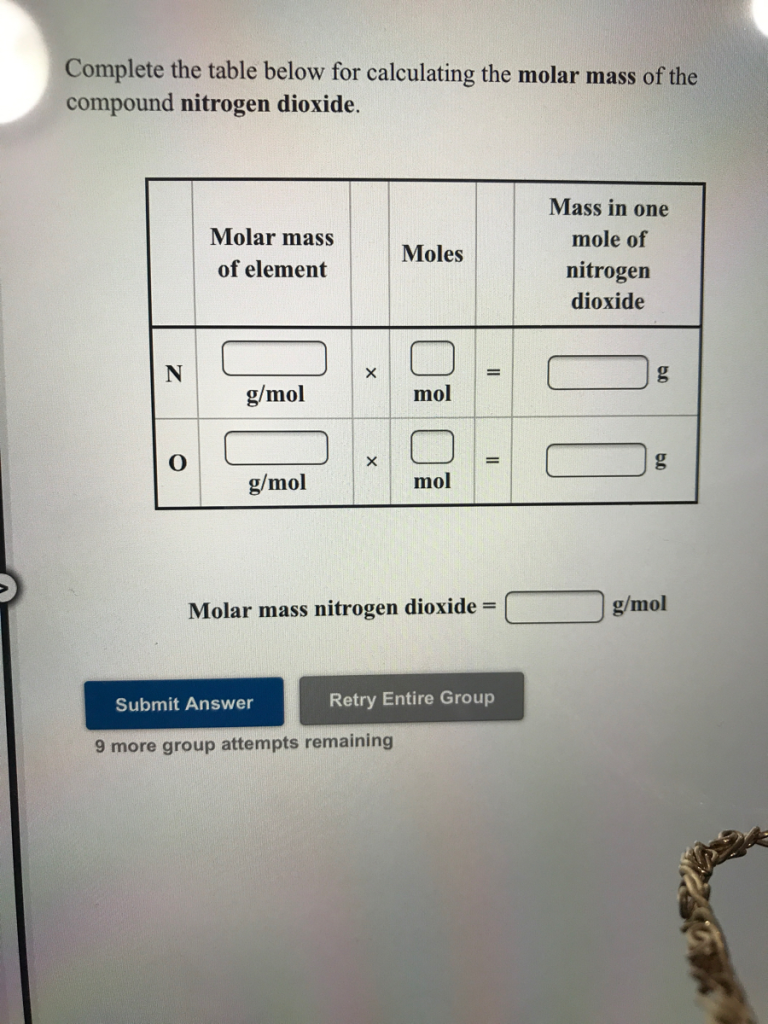
Complete the table below for calculating the molar mass of the compound nitrogen dioxide.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The molar mass of a compound is calculated by summing the molar masses of all the atoms in its chemical formula. For nitrogen dioxide ((NO_2)), we use the periodic table to find the atomic masses of nitrogen (N) and oxygen (O).
Table for Molar Mass of (NO_2)
| Element | Number of Atoms | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Total Contribution (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | 1 | 14.01 | (1 \times 14.01 = 14.01) |
| Oxygen (O) | 2 | 16.00 | (2 \times 16.00 = 32.00) |
| Total | (14.01 + 32.00 = 46.01) |
Explanation of the Calculation
- Determine the Atomic Masses:
- The atomic mass of nitrogen (N) is (14.01 \, \text{g/mol}), and oxygen (O) is (16.00 \, \text{g/mol}), as found on the periodic table.
- Count the Number of Atoms:
- In one molecule of (NO_2), there is 1 nitrogen atom and 2 oxygen atoms.
- Multiply Atomic Mass by the Number of Atoms:
- For nitrogen: (14.01 \, \text{g/mol} \times 1 = 14.01 \, \text{g/mol})
- For oxygen: (16.00 \, \text{g/mol} \times 2 = 32.00 \, \text{g/mol})
- Add the Contributions:
- Total molar mass of (NO_2 = 14.01 \, \text{g/mol} + 32.00 \, \text{g/mol} = 46.01 \, \text{g/mol}).
- Significance of Molar Mass:
- The molar mass allows chemists to convert between moles and grams, facilitating stoichiometric calculations in chemical reactions. For example, one mole of (NO_2) weighs (46.01 \, \text{g}).
- Applications:
- The calculated molar mass is used in various fields, such as environmental science (studying (NO_2) emissions) and industrial chemistry (where (NO_2) is a key intermediate in processes like nitric acid production).
In summary, the molar mass of (NO_2) is (46.01 \, \text{g/mol}), calculated by summing the atomic masses of all its constituent atoms based on their respective quantities in the compound.