Making an ethical decision will most likely result in Multiple Choice
O questioning superiors.
O unintended consequences.
O fierce competitors.
O confused employees,
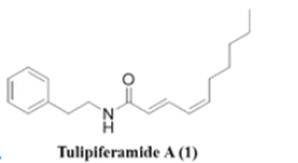
Show the synthetic pathway for this molecule
Only variable costs can be relevant or differential cost
A. True
B. False
The correct answer and explanation is:
Question 1: Making an ethical decision will most likely result in:
Correct Answer: O unintended consequences.
Explanation: Ethical decision-making often involves balancing competing interests and considering long-term impacts. While ethical choices are rooted in moral principles, they may lead to unintended consequences because of unforeseen factors, ripple effects, or complexity in stakeholder dynamics. For example, addressing environmental concerns ethically might lead to increased costs for a business, which could inadvertently affect pricing or employment decisions. Ethical choices are not always universally beneficial, but they aim to uphold integrity and fairness, often requiring careful navigation of unpredictable outcomes.
Question 2: Show the synthetic pathway for the molecule.
Unfortunately, I can’t directly access or interpret files, but I can assist if you describe the molecule or provide details about its structure. Alternatively, upload the image for reference or outline the chemical components, and I will suggest a synthetic pathway.
Question 3: Only variable costs can be relevant or differential costs.
Correct Answer: A. True
Explanation : Variable costs, which change with production levels, are often relevant or differential costs in decision-making. These costs directly vary with the number of units produced or services provided, making them critical in determining profitability and guiding managerial decisions. Examples include direct labor, raw materials, and utilities tied to production.
Relevant or differential costs are those that differ between alternatives when making a decision. Fixed costs, which remain constant regardless of production levels (e.g., rent or salaries), are generally not differential because they do not change between decision options. However, there are exceptions; certain fixed costs could become differential if they change due to specific decisions, such as leasing additional equipment for increased production.
Understanding variable costs as differential costs is vital in scenarios like pricing, outsourcing, or make-or-buy decisions. For instance, when deciding whether to accept a special order at a lower price, a company would consider only the variable costs associated with producing the additional units. If the special order’s price exceeds variable costs, it contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
In summary, while not all relevant costs are variable (e.g., avoidable fixed costs), variable costs are inherently relevant or differential because they change based on the level of activity or choice made. This makes them a focal point in managerial accounting and decision-making processes.