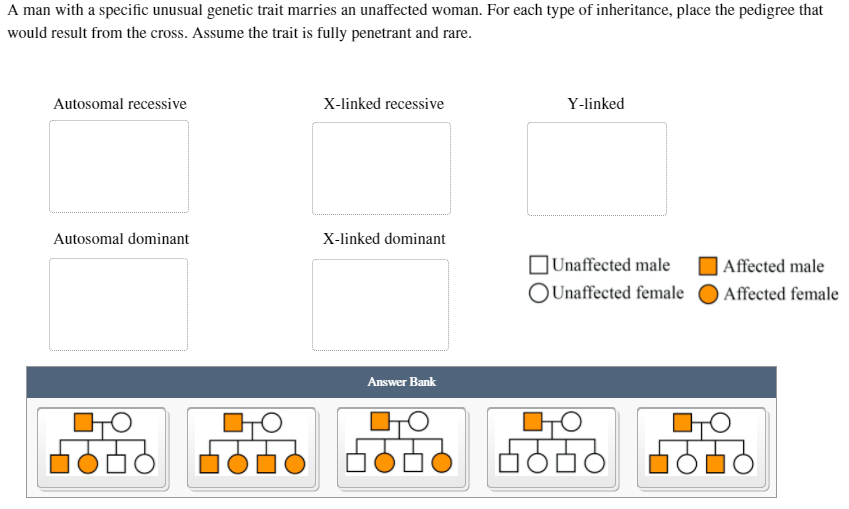
A man with a specific unusual genetic trait marries an unaffected woman. For each type of inheritance, place the pedigree that would result from the cross. Assume the trait is fully penetrant and rare. Autosomal recessive X-linked recessive Y-linked Autosomal dominant X-linked dominant |Unaffected male |Affected male OUnaffected female Affected female Answer Bank 오모오모 None
The correct answer and explanation is:
To determine the correct pedigree for each type of inheritance based on the situation described (a man with a specific genetic trait marries an unaffected woman), we’ll evaluate each inheritance pattern. Here’s a guide to match the pedigrees:
1. Autosomal Recessive
- Both copies of the gene must be affected for an individual to express the trait.
- The affected man is homozygous recessive (aa).
- The unaffected woman is likely homozygous dominant (AA) (since the trait is rare).
- All offspring will inherit one dominant allele (A) and one recessive allele (a), making them carriers but not affected.
- Pedigree outcome: None of the children are affected.
2. Autosomal Dominant
- A single copy of the dominant allele is sufficient to express the trait.
- The affected man is heterozygous (Aa) (since the trait is rare).
- The unaffected woman is homozygous recessive (aa).
- Each child has a 50% chance of inheriting the dominant allele and being affected.
- Pedigree outcome: Half of the children are affected.
3. X-linked Recessive
- The trait is linked to the X chromosome.
- The affected man has the trait on his single X chromosome (XᵃY).
- The unaffected woman has two normal X chromosomes (XᴬXᴬ).
- Sons inherit their X chromosome from the mother, so none of the sons are affected.
- Daughters inherit one X chromosome from the father and one from the mother, making all daughters carriers (XᴬXᵃ).
- Pedigree outcome: No affected children, but all daughters are carriers.
4. X-linked Dominant
- A single copy of the dominant allele on the X chromosome is sufficient to express the trait.
- The affected man has the trait on his X chromosome (XᴬY).
- The unaffected woman has two normal X chromosomes (XᴬXᴬ).
- All daughters inherit the affected X chromosome from the father and are affected.
- No sons are affected, as they inherit the Y chromosome from the father.
- Pedigree outcome: All daughters are affected, and all sons are unaffected.
5. Y-linked
- The trait is linked to the Y chromosome and is passed from father to son only.
- The affected man has the trait on his Y chromosome (XYᵃ).
- The unaffected woman does not contribute to the Y chromosome.
- All sons are affected, and no daughters are affected, as they do not inherit the Y chromosome.
- Pedigree outcome: All sons are affected, and no daughters are affected.
Let me know if you’d like further assistance matching these descriptions to the specific pedigree diagrams from your file.