Identify the highlighted functional groups in this molecule
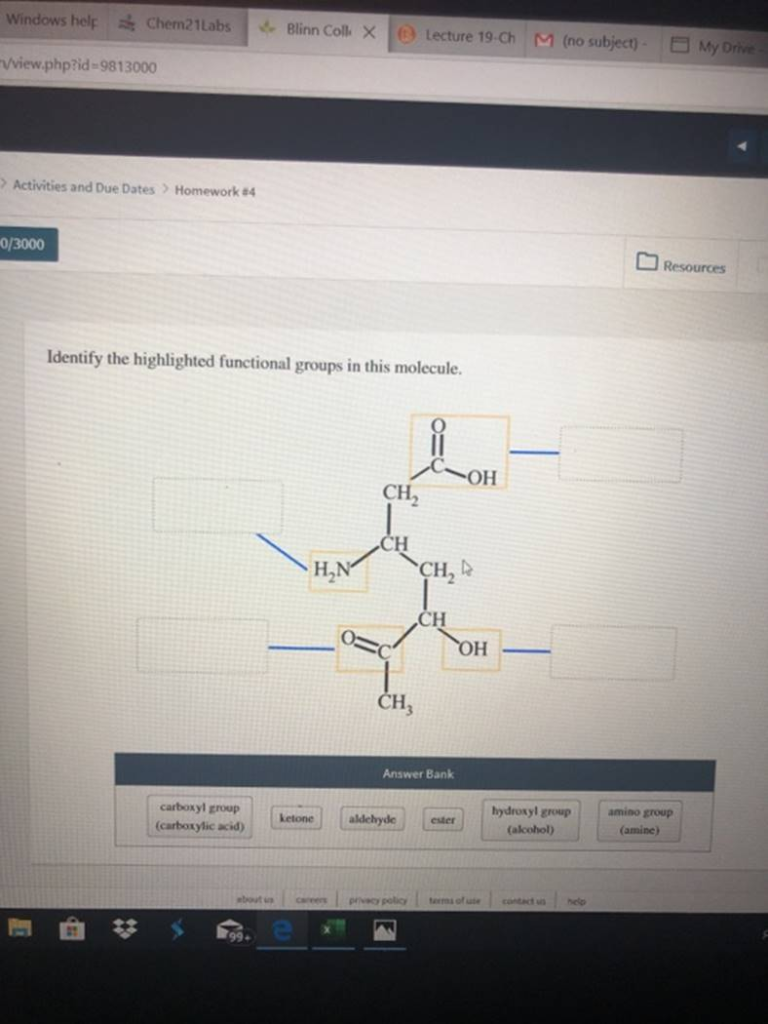
carboxyl group (carboxylic acid) ketone aldehyde ester hydroxyl group (alcohol amino group (amine)
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
To accurately identify the functional groups in the molecule from the image, let’s examine each part of the structure. Here’s the breakdown:
Functional Groups Present in the Molecule:
- Carboxyl group (Carboxylic acid):
- Look for a -COOH group, where a carbon is double-bonded to an oxygen (C=O) and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH).
- This is present in the molecule as a functional group.
- Ketone:
- Look for a C=O group where the carbon is bonded to two other carbons.
- The molecule does not contain a ketone group.
- Aldehyde:
- Look for a -CHO group, where a carbon is double-bonded to oxygen and single-bonded to a hydrogen.
- The molecule does not have an aldehyde group.
- Ester:
- Look for a -COOR group, where a carbon is double-bonded to oxygen (C=O) and also bonded to another oxygen atom (R-O).
- The molecule does not contain an ester group.
- Hydroxyl group (Alcohol):
- Look for an -OH group attached directly to a carbon atom.
- This is present in the molecule as a hydroxyl group.
- Amino group (Amine):
- Look for a -NH2, -NHR, or -NR2 group attached to a carbon atom.
- This is present in the molecule as an amino group.
Explanation (300 words):
The molecule in the image contains three key functional groups: carboxyl (carboxylic acid), hydroxyl (alcohol), and amino (amine) groups. Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
- Carboxyl group: The carboxylic acid group (-COOH) is characterized by a carbon atom bonded to both a hydroxyl (-OH) group and a carbonyl group (C=O). This group imparts acidic properties to the molecule, as the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group can dissociate to form H⁺ ions.
- Hydroxyl group: The hydroxyl group (-OH) appears independently from the carboxyl group in the molecule. It is responsible for the molecule’s ability to engage in hydrogen bonding, affecting solubility and boiling point.
- Amino group: The amino group (-NH2) in this molecule is a basic group that can accept protons (H⁺), contributing to its reactivity and importance in biochemical processes such as protein formation.
Understanding these functional groups is critical because they define the molecule’s chemical reactivity, polarity, and interactions with other molecules. This knowledge is particularly vital in fields like biochemistry, where molecules with carboxyl, amino, and hydroxyl groups play essential roles in life processes.