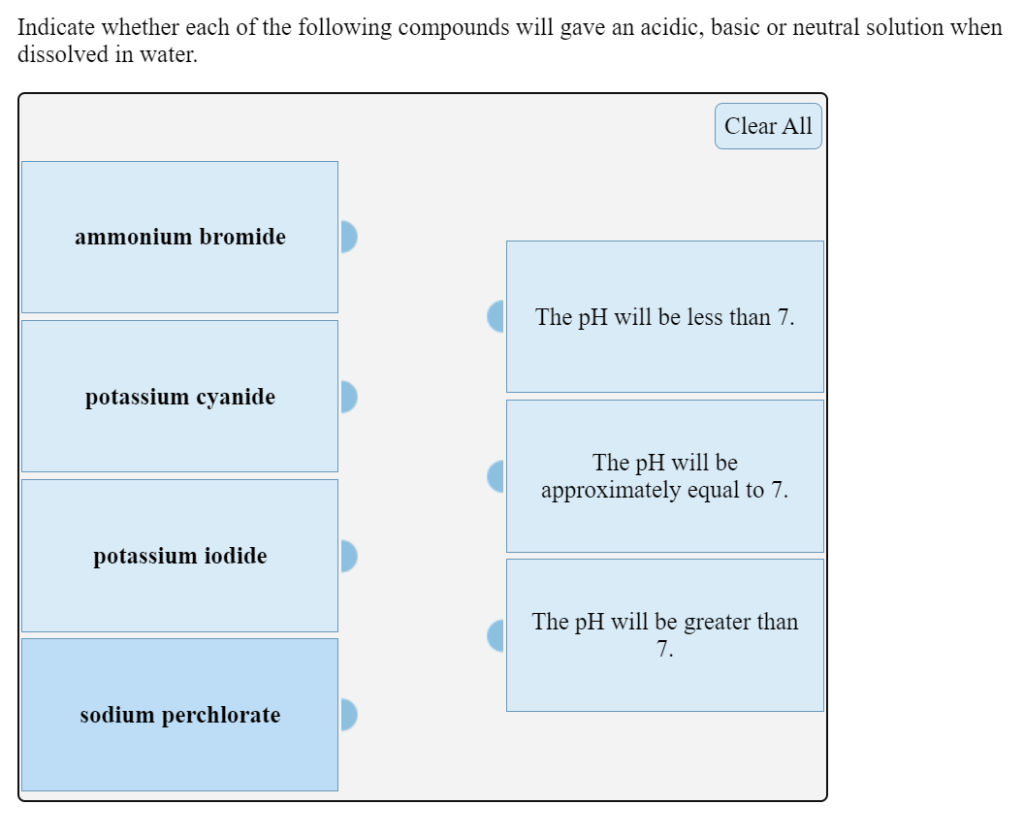
Indicate whether each of the following compounds will gave an acidic, basic or neutral solution when dissolved in water. Clear All ammonium bromide The pH will be less than 7. potassium cyanide The pH will be approximately equal to 7. potassium iodide The pH will be greater than 7. sodium perchlorate
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
When salts dissolve in water, they dissociate into their constituent ions, which can influence the solution’s pH based on their acidic or basic properties. Let’s analyze each compound:
1. Ammonium Bromide (NH₄Br):
- Dissociation: NH₄Br → NH₄⁺ + Br⁻
- Analysis:
- NH₄⁺ (Ammonium ion): Acts as a weak acid; it can donate a proton (H⁺) to water, forming hydronium ions (H₃O⁺), which increase the solution’s acidity.
- Br⁻ (Bromide ion): The conjugate base of a strong acid (HBr) and does not significantly affect pH.
- Conclusion: The presence of NH₄⁺ makes the solution acidic, resulting in a pH less than 7.
2. Potassium Cyanide (KCN):
- Dissociation: KCN → K⁺ + CN⁻
- Analysis:
- K⁺ (Potassium ion): The conjugate acid of a strong base (KOH) and does not affect pH.
- CN⁻ (Cyanide ion): Acts as a weak base; it can accept a proton from water, producing hydroxide ions (OH⁻), which increase the solution’s basicity.
- Conclusion: The presence of CN⁻ makes the solution basic, resulting in a pH greater than 7.
3. Potassium Iodide (KI):
- Dissociation: KI → K⁺ + I⁻
- Analysis:
- K⁺ (Potassium ion): Does not affect pH.
- I⁻ (Iodide ion): The conjugate base of a strong acid (HI) and does not affect pH.
- Conclusion: Both ions are neutral concerning pH, so the solution remains neutral with a pH approximately equal to 7.
4. Sodium Perchlorate (NaClO₄):
- Dissociation: NaClO₄ → Na⁺ + ClO₄⁻
- Analysis:
- Na⁺ (Sodium ion): Does not affect pH.
- ClO₄⁻ (Perchlorate ion): The conjugate base of a strong acid (HClO₄) and does not affect pH.
- Conclusion: Both ions are neutral concerning pH, so the solution remains neutral with a pH approximately equal to 7.
Summary:
- Ammonium Bromide: Acidic solution (pH < 7)
- Potassium Cyanide: Basic solution (pH > 7)
- Potassium Iodide: Neutral solution (pH ≈ 7)
- Sodium Perchlorate: Neutral solution (pH ≈ 7)
Understanding the nature of the ions produced upon dissociation helps predict the resulting pH of the solution. Ions that are conjugates of strong acids or bases typically do not affect pH, while those from weak acids or bases can hydrolyze, altering the pH accordingly.