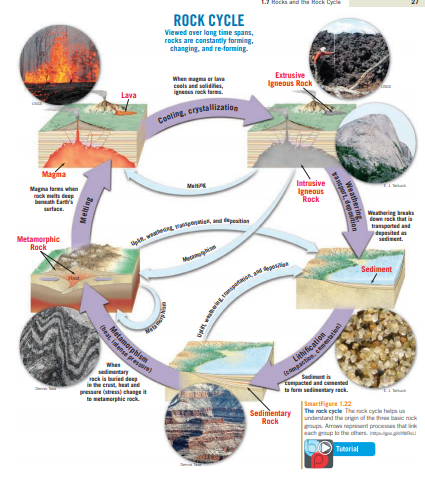
How does the rock cycle diagram, particularly the process arrows, support the fact that sedimentary rock is the most abundant rock type on the surface of Earth?
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The rock cycle diagram illustrates how Earth’s materials transform between three primary rock types: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary. The arrows in the diagram represent processes such as weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, cementation, melting, cooling, and metamorphism. These arrows and processes explain why sedimentary rocks are the most abundant rock type on Earth’s surface.
Correct Answer:
Sedimentary rocks are the most abundant on Earth’s surface because the processes that form them—weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, and cementation—are highly surface-oriented and continuous over geologic time.
Explanation:
- Weathering and Erosion:
Arrows from all rock types to sediments in the diagram indicate that igneous, metamorphic, and even existing sedimentary rocks are continually broken down by weathering and erosion. These processes are driven by surface conditions like wind, water, and temperature fluctuations, making them widespread and persistent. - Transportation and Deposition:
The eroded materials are transported by agents such as rivers, glaciers, and wind before being deposited in basins, lakes, and oceans. These areas are common on Earth’s surface, ensuring a constant supply of sediments. - Compaction and Cementation:
Arrows leading from sediments to sedimentary rocks highlight how layers of sediments are compacted and cemented over time to form sedimentary rocks. These processes occur in shallow environments like riverbeds, deltas, and ocean floors, contributing to the prevalence of sedimentary rocks on the surface. - Surface Orientation:
Unlike igneous rocks, which form primarily from magma deep within the Earth, or metamorphic rocks, which require extreme pressure and heat below the surface, sedimentary rocks form under conditions that dominate the Earth’s crust.
The rock cycle diagram emphasizes that sedimentary rocks are the product of surface-driven processes that recycle Earth’s materials continuously, leading to their widespread presence and abundance on the surface.