What is the “R” in organic chemistry mean? And what does R’ mean?
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
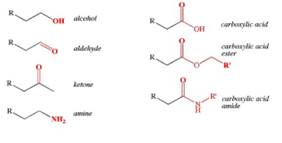
In organic chemistry, the symbol “R” represents a generic alkyl group, which is essentially any group that can be derived from an alkane (a hydrocarbon with only single bonds) by removing one hydrogen atom. The “R” is used as a placeholder for any group of atoms that may be attached to a molecule, typically denoting a part of a molecule that is a hydrocarbon chain or any structure that can be derived from an alkane.
For example, if we have a molecule such as an alcohol or an ether, and we don’t want to specify exactly which alkyl group is attached, we use “R” in place of the alkyl group. It could represent a methyl group (-CH₃), an ethyl group (-C₂H₅), or any larger hydrocarbon chain.
When we see “R'”, it typically refers to a different alkyl group than “R” within the same molecule or reaction. For instance, in a chemical reaction where two groups are exchanging, “R” might refer to one group (e.g., a methyl group) and “R'” might refer to another (e.g., an ethyl group).
These symbols help simplify the representation of chemical structures and reactions, as the exact nature of the alkyl groups might not be important for the specific purpose at hand. This allows chemists to focus on the core reaction or structure without getting bogged down in specifying every detail of the groups involved. The use of “R” and “R'” is very common in reaction mechanisms and in describing functional groups, particularly when the identity of the group is not central to the chemistry being described.