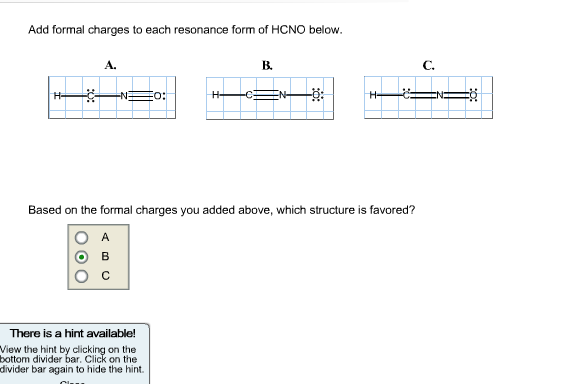
Add formal charges to each resonance form of HCNO below. Based on the formal charges you added above, which structure is favored?
The correct answer and explanation is:
To determine the formal charges for each resonance form of HCNO and decide which structure is favored, we calculate the formal charge for each atom in all resonance forms using the formula: Formal Charge=Valence Electrons−(Non-bonding Electrons+Bonding Electrons2)\text{Formal Charge} = \text{Valence Electrons} – (\text{Non-bonding Electrons} + \frac{\text{Bonding Electrons}}{2})
Here’s the step-by-step process:
Resonance Form 1
Structure: H–C≡N–O (with a single bond to oxygen)
- H (Hydrogen)
Valence electrons: 1
Non-bonding electrons: 0
Bonding electrons: 2 Formal Charge=1−(0+22)=0\text{Formal Charge} = 1 – (0 + \frac{2}{2}) = 0 - C (Carbon)
Valence electrons: 4
Non-bonding electrons: 0
Bonding electrons: 8 (two triple bonds, one single bond) Formal Charge=4−(0+82)=0\text{Formal Charge} = 4 – (0 + \frac{8}{2}) = 0 - N (Nitrogen)
Valence electrons: 5
Non-bonding electrons: 2
Bonding electrons: 6 Formal Charge=5−(2+62)=0\text{Formal Charge} = 5 – (2 + \frac{6}{2}) = 0 - O (Oxygen)
Valence electrons: 6
Non-bonding electrons: 6
Bonding electrons: 2 Formal Charge=6−(6+22)=−1\text{Formal Charge} = 6 – (6 + \frac{2}{2}) = -1
Summary: Formal charges: H = 0, C = 0, N = 0, O = -1.
Resonance Form 2
Structure: H–C=N=O (double bonds to both N and O)
- H (Hydrogen)
Formal Charge = 0 (same as above). - C (Carbon)
Valence electrons: 4
Non-bonding electrons: 0
Bonding electrons: 8 Formal Charge=4−(0+82)=0\text{Formal Charge} = 4 – (0 + \frac{8}{2}) = 0 - N (Nitrogen)
Valence electrons: 5
Non-bonding electrons: 2
Bonding electrons: 6 Formal Charge=5−(2+62)=0\text{Formal Charge} = 5 – (2 + \frac{6}{2}) = 0 - O (Oxygen)
Valence electrons: 6
Non-bonding electrons: 4
Bonding electrons: 4 Formal Charge=6−(4+42)=0\text{Formal Charge} = 6 – (4 + \frac{4}{2}) = 0
Summary: Formal charges: H = 0, C = 0, N = 0, O = 0.
Resonance Form 3
Structure: H–C=N–O⁻ (single bond to N, triple bond to O, with a negative charge on oxygen)
- H (Hydrogen)
Formal Charge = 0 (same as above). - C (Carbon)
Valence electrons: 4
Non-bonding electrons: 0
Bonding electrons: 8 Formal Charge=4−(0+82)=0\text{Formal Charge} = 4 – (0 + \frac{8}{2}) = 0 - N (Nitrogen)
Valence electrons: 5
Non-bonding electrons: 2
Bonding electrons: 6 Formal Charge=5−(2+62)=0\text{Formal Charge} = 5 – (2 + \frac{6}{2}) = 0 - O (Oxygen)
Valence electrons: 6
Non-bonding electrons: 6
Bonding electrons: 2 Formal Charge=6−(6+22)=−1\text{Formal Charge} = 6 – (6 + \frac{2}{2}) = -1
Summary: Formal charges: H = 0, C = 0, N = 0, O = -1.
Which Structure is Favored?
- The second resonance form (H–C=N=O) has formal charges of 0 on all atoms, making it the most stable and favored structure because resonance forms with minimized formal charges are generally more stable.