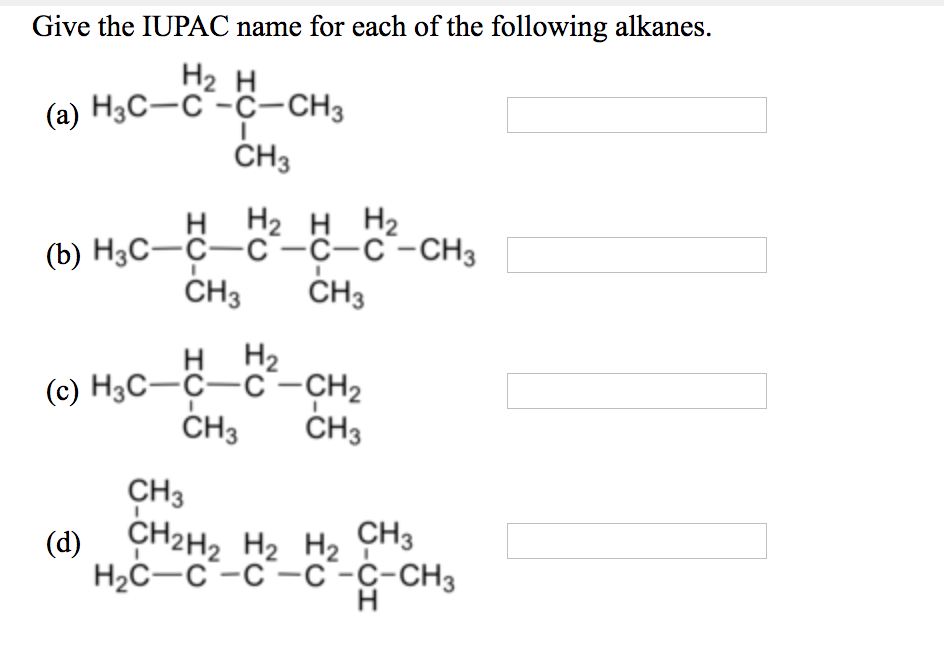
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alkanes. ….
The correct answer and explanation is:
The alkanes shown in the provided image appear to be:
- CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₃
- IUPAC Name: Butane
Explanation: This compound consists of a straight-chain alkane with four carbon atoms. According to the IUPAC nomenclature system, the prefix “but-” is used for a chain of four carbons, and the suffix “-ane” indicates that it is a saturated hydrocarbon (an alkane). There are no substituents or branches, so the name is straightforward.
- IUPAC Name: Butane
- CH₃CH(CH₃)CH₃
- IUPAC Name: 2-Methylpropane
Explanation: This is a branched alkane with three carbons in the main chain (propane). A methyl group (-CH₃) is attached to the second carbon. The parent chain is named “propane,” and the substituent is named “methyl.” The number “2” specifies the position of the methyl group along the chain. It is also commonly known as isobutane.
- IUPAC Name: 2-Methylpropane
- CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂CH₃
- IUPAC Name: Pentane
Explanation: This compound is a straight-chain alkane with five carbon atoms. The prefix “pent-” corresponds to five carbons, and the suffix “-ane” denotes that it is an alkane. Since the chain is unbranched, no additional naming is required.
- IUPAC Name: Pentane
Detailed Explanation of IUPAC Naming Rules:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) system provides a standardized method for naming organic compounds based on their structure. For alkanes:
- Identify the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. This determines the parent name (e.g., methane, ethane, propane, etc.).
- Number the chain so that substituents (if any) receive the lowest possible numbers.
- Name the substituents (alkyl groups) and indicate their positions on the main chain.
- Combine the names, placing substituents alphabetically before the parent name and using hyphens to separate numbers from words.
By following these steps, each compound is named systematically, ensuring clarity and consistency across the field of organic chemistry.