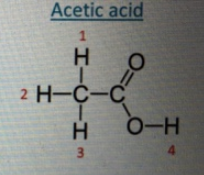
The Lewis structure of acetic acid (CH3COOH) is shown on the right. Its aqueous solution is described by an equilibrium:
CH3COOH(aq)CH3COO (aq) + H(aq)
Which of the four numbered Hydrogens in the Lewis structure yields H'(aq) appearing in the above chemical equilibrium?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C)3 (D) 4
(E) Any one of the equivalent 1-3 position
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
To answer this question, let’s carefully analyze the structure of acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and its dissociation in aqueous solution.
Lewis Structure of Acetic Acid:
Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) consists of a methyl group (-CH₃) and a carboxyl group (-COOH). The carboxyl group consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O) and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH). The other part of the molecule is the methyl group (-CH₃), which is composed of a carbon atom single-bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
The structure looks like this:
H O
| ||
H-C-C-O-H
|
HThe numbered hydrogens (H₁, H₂, H₃, and H₄) refer to the four hydrogen atoms in the molecule, three of which are attached to the methyl group (H₁, H₂, and H₃), and one attached to the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (H₄).
Dissociation of Acetic Acid in Aqueous Solution:
In an aqueous solution, acetic acid dissociates according to the equilibrium:
[
CH₃COOH(aq) \rightleftharpoons CH₃COO⁻(aq) + H⁺(aq)
]
Here, the acetic acid molecule donates a proton (H⁺) from the carboxyl group (the -OH part of the carboxyl group).
Which Hydrogen Donates H⁺?
In this dissociation, it is the hydrogen attached to the oxygen of the hydroxyl group (H₄) that dissociates to form H⁺. This is because the O-H bond is polar and relatively weak compared to the C-H bonds in the methyl group. Therefore, it is more likely that the hydrogen from the hydroxyl group will be released as a proton (H⁺).
Conclusion:
The correct answer is (D) 4, as it is the hydrogen in the hydroxyl group (-OH) that dissociates to yield H⁺ in the equilibrium reaction.
In summary:
- The hydrogens in positions 1, 2, and 3 are part of the methyl group and are not involved in the dissociation.
- The hydrogen in position 4 is the one that dissociates to form H⁺ in the aqueous solution, which is a key characteristic of the behavior of carboxylic acids like acetic acid in water.
Thus, H₄ is the hydrogen that yields H⁺(aq).