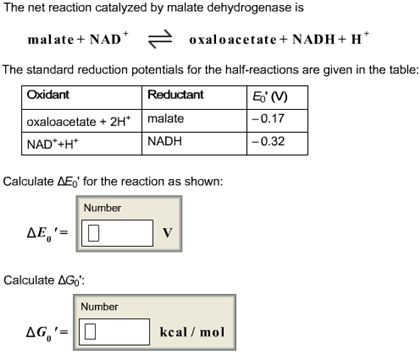
The net reaction catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase is malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H + The standard reduction potentials for the half-reactions are given in the table: Calculate Delta E0′ for the reaction as shown: Delta E0′ = V Calculate Delta G0′: Delta G0 = kcal / mol
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The reaction catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase is:
Malate + NAD⁺ ⇌ Oxaloacetate + NADH + H⁺
To calculate the standard change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG°’) and the standard cell potential (ΔE°’) for this reaction, we can use the standard reduction potentials provided for the half-reactions:
- Oxaloacetate + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ Malate: E°’ = -0.17 V
- NAD⁺ + H⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ NADH: E°’ = -0.32 V
Calculating ΔE°’:
The standard cell potential (ΔE°’) is calculated by subtracting the reduction potential of the oxidation half-reaction from that of the reduction half-reaction:
ΔE°’ = E°’ (reduction) – E°’ (oxidation)
In this reaction, malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate, and NAD⁺ is reduced to NADH. Therefore, the oxidation half-reaction is:
Malate ⇌ Oxaloacetate + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
The reduction half-reaction is:
NAD⁺ + H⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ NADH
Thus, ΔE°’ = (-0.32 V) – (-0.17 V) = -0.15 V
Calculating ΔG°’:
The standard change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG°’) is related to the standard cell potential (ΔE°’) by the equation:
ΔG°’ = -nFΔE°’
Where:
- n = number of moles of electrons transferred (2 electrons in this reaction)
- F = Faraday’s constant (96,485 C/mol)
- ΔE°’ = standard cell potential (in volts)
Substituting the known values:
ΔG°’ = -2 × 96,485 C/mol × (-0.15 V)
ΔG°’ = 28,946 J/mol
Since 1 kcal = 4,184 J, ΔG°’ = 28,946 J/mol ÷ 4,184 J/kcal ≈ 6.9 kcal/mol
Conclusion:
The standard cell potential (ΔE°’) for the malate dehydrogenase reaction is -0.15 V, and the standard change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG°’) is approximately 6.9 kcal/mol.
A negative ΔE°’ indicates that the reaction is non-spontaneous under standard conditions. The positive ΔG°’ value further confirms that the reaction requires energy input to proceed. In biological systems, this reaction is coupled with other reactions to drive the overall metabolic processes.