What is the product of the following reaction? NaNH2 (
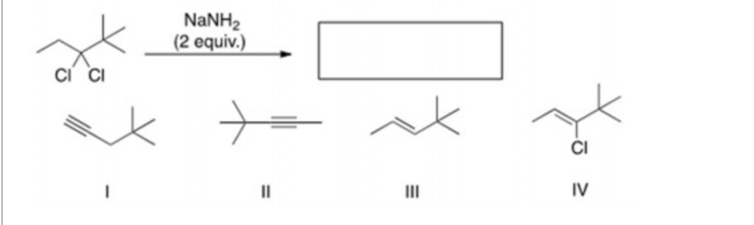
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Sodium amide (NaNH₂) is a potent base and nucleophile widely utilized in organic synthesis. Its strong basicity enables it to deprotonate weak acids, while its nucleophilicity allows it to participate in substitution reactions.
Deprotonation of Terminal Alkynes:
One of the primary applications of NaNH₂ is the deprotonation of terminal alkynes to form acetylide ions. These acetylide ions are valuable intermediates in organic synthesis, capable of undergoing nucleophilic substitution reactions with alkyl halides to form new carbon-carbon bonds. For example, treating a terminal alkyne with NaNH₂ generates the corresponding acetylide ion, which can then react with an alkyl halide to produce an internal alkyne. (Master Organic Chemistry)
Elimination Reactions:
NaNH₂ also facilitates elimination reactions, particularly the double dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides to yield alkynes. In this process, NaNH₂ abstracts two equivalents of hydrogen halide from a vicinal dihalide, resulting in the formation of a carbon-carbon triple bond. This method is commonly employed to synthesize alkynes from dihalides. (Chemistry LibreTexts)
Nucleophilic Substitution:
As a strong nucleophile, NaNH₂ can participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions. For instance, when NaNH₂ reacts with methyl iodide (CH₃I), it displaces the iodide ion to form methylamine (CH₃NH₂). This reaction exemplifies NaNH₂’s ability to act as a nucleophile, replacing a leaving group with an amine group. (Brainly)
Safety Considerations:
While NaNH₂ is a versatile reagent, it is highly reactive and can decompose violently upon contact with water, producing ammonia and sodium hydroxide. Therefore, it must be handled with caution, stored under an inert atmosphere, and used in anhydrous conditions to prevent unwanted reactions. (Wikipedia)
In summary, sodium amide is a powerful reagent in organic chemistry, facilitating deprotonation, elimination, and nucleophilic substitution reactions. Its strong basicity and nucleophilicity make it indispensable for synthesizing a wide range of organic compounds.