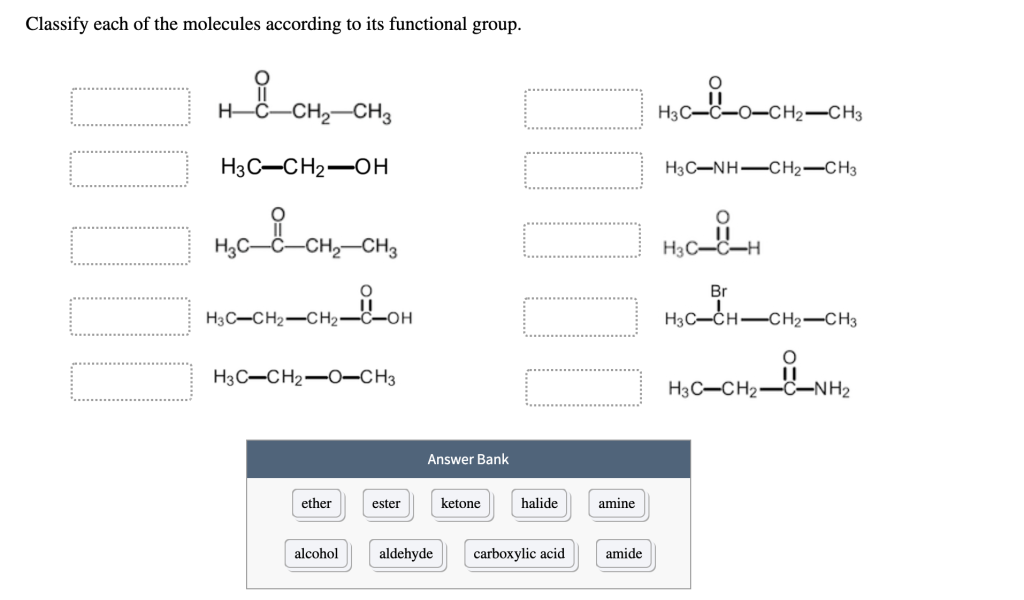
Classify each of the molecules according to its functional group. OOOO || HC–CH2CH3 H3C-CH₂-OH _i_CH₂ H3C-C-CH₂-CH3 H3C-CH₂-CH₂-C-OH OH H3C-CH₂-O-CH3 ether alcohol ester Answer Bank ketone DOUDO halide aldehyde carboxylic acid amine amide H3C-C-O-CH2-CH3 H3C—NH–CH2–CH3 H3C-C-H Br H3C-CH-CH₂-CH3 || H3C–CH2–C_NH2
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Based on the provided molecular structures, I will classify each one according to its functional group. Below is a breakdown of the molecules and their functional groups:
- HC-CH₂CH₃ (C₄H₈):
- Functional Group: Alkene.
- Explanation: This structure represents an alkene, as it contains a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C), which is characteristic of alkene functional groups.
- H₃C-CH₂-OH (C₂H₆O):
- Functional Group: Alcohol.
- Explanation: This molecule has a hydroxyl group (-OH), which is characteristic of alcohols. The presence of this group makes it an alcohol.
- H₃C-C-CH₂-CH₃ (C₄H₈O):
- Functional Group: Ketone.
- Explanation: The structure has a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two other carbon atoms, which is characteristic of a ketone.
- H₃C-CH₂-CH₂-C-OH (C₄H₈O₂):
- Functional Group: Carboxylic Acid.
- Explanation: The presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH) indicates that this molecule is a carboxylic acid. The -COOH group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group.
- H₃C-CH₂-O-CH₃ (C₄H₁₀O):
- Functional Group: Ether.
- Explanation: This molecule contains an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl groups (C–O–C), which is characteristic of an ether functional group.
- H₃C-NH-CH₂-CH₃ (C₄H₁₁N):
- Functional Group: Amine.
- Explanation: The presence of an amino group (-NH₂) attached to a carbon chain identifies this molecule as an amine.
- H₃C-C-H (C₃H₆):
- Functional Group: Alkene.
- Explanation: This molecule contains a double bond between two carbon atoms, indicating it is an alkene.
- H₃C-CH₂-C-NH₂ (C₄H₉N):
- Functional Group: Amide.
- Explanation: This molecule contains a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom, which is characteristic of an amide functional group.
- H₃C-C-O-CH₂-CH₃ (C₄H₈O₂):
- Functional Group: Ester.
- Explanation: The ester functional group consists of a carbonyl group attached to an oxygen atom, which is also bonded to an alkyl group. This molecule fits the ester description.
- H₃C-Br (C₂H₅Br):
- Functional Group: Halide.
- Explanation: The presence of a halogen (bromine, Br) attached to a carbon atom indicates that this molecule is a halide.
Conclusion:
- Alcohol: H₃C-CH₂-OH.
- Alkene: HC-CH₂CH₃, H₃C-CH-H.
- Ketone: H₃C-C-CH₂-CH₃.
- Carboxylic Acid: H₃C-CH₂-CH₂-C-OH.
- Ether: H₃C-CH₂-O-CH₃.
- Amine: H₃C-NH-CH₂-CH₃.
- Amide: H₃C-CH₂-C-NH₂.
- Ester: H₃C-C-O-CH₂-CH₃.
- Halide: H₃C-Br.
These classifications depend on the functional groups each molecule contains, which dictate their chemical reactivity and properties. Each group has unique structural features such as hydroxyl, carbonyl, amine, and halogen atoms that define their roles in organic chemistry.