Using the Nernst equation, complete the following table:
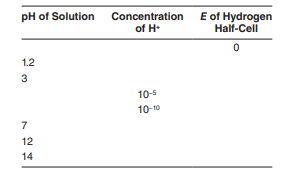
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The Nernst equation is often used in electrochemistry to calculate the equilibrium potential for an ion based on its concentration gradient across a membrane. The equation is:
[
E = \frac{RT}{zF} \ln \left( \frac{[ion]{out}}{[ion]{in}} \right)
]
Where:
- ( E ) is the equilibrium potential (in volts),
- ( R ) is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K),
- ( T ) is the temperature in Kelvin (usually assumed to be 298 K),
- ( z ) is the valence of the ion (for example, +1 for potassium, Na+),
- ( F ) is the Faraday constant (approximately 96485 C/mol),
- ([ion]{out}) and ([ion]{in}) are the ion concentrations outside and inside the membrane, respectively.
Could you share the table’s specific data (such as ion concentrations and ion charge) so that I can assist you in completing it?