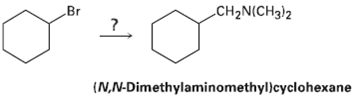
How would you use the reaction of an amide with LiAlH4 as the key step is going from bromo cyclohexane to (N, N-dimethylaminomethyl) cyclohexane? Write all the steps in the reactionsequence.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
To synthesize (N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)cyclohexane from bromocyclohexane using the reduction of an amide with lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH₄) as the key step, follow this sequence:
- Formation of the Grignard Reagent:
React bromocyclohexane with magnesium metal in dry ether to form cyclohexylmagnesium bromide, a Grignard reagent. [ \text{C}6\text{H}{11}\text{Br} + \text{Mg} \xrightarrow{\text{ether}} \text{C}6\text{H}{11}\text{MgBr} ] - Carboxylation to Benzoic Acid:
Add carbon dioxide (CO₂) to the Grignard reagent, followed by acidic work-up, to yield benzoic acid (C₆H₅COOH). [ \text{C}6\text{H}{11}\text{MgBr} + \text{CO}_2 \xrightarrow{\text{acid work-up}} \text{C}_6\text{H}_5\text{COOH} ] - Conversion to Benzoyl Chloride:
React benzoic acid with thionyl chloride (SOCl₂) to form benzoyl chloride (C₆H₅COCl). [ \text{C}_6\text{H}_5\text{COOH} + \text{SOCl}_2 \rightarrow \text{C}_6\text{H}_5\text{COCl} + \text{SO}_2 + \text{HCl} ] - Synthesis of N,N-Dimethylbenzamide:
React benzoyl chloride with dimethylamine (CH₃NH₂) to produce N,N-dimethylbenzamide. [ \text{C}_6\text{H}_5\text{COCl} + \text{CH}_3\text{NH}_2 \rightarrow \text{C}_6\text{H}_5\text{CON(CH}_3\text{)}_2 + \text{HCl} ] - Reduction to (N,N-Dimethylaminomethyl)cyclohexane:
Reduce N,N-dimethylbenzamide with LiAlH₄ in dry ether to obtain (N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)cyclohexane. [ \text{C}6\text{H}_5\text{CON(CH}_3\text{)}_2 + \text{LiAlH}_4 \xrightarrow{\text{ether}} \text{C}_6\text{H}{11}\text{N(CH}_3\text{)}_2 + \text{LiAlH}_3\text{O} ]
Explanation:
- Grignard Reagent Formation: Bromocyclohexane reacts with magnesium in dry ether to form a Grignard reagent, which is a strong nucleophile.
- Carboxylation: The Grignard reagent adds CO₂ to form a magnesium salt of benzoic acid, which, upon acidic work-up, yields benzoic acid.
- Acylation: Benzoyl chloride reacts with dimethylamine to form N,N-dimethylbenzamide through nucleophilic acyl substitution.
- Reduction: LiAlH₄ reduces the amide group in N,N-dimethylbenzamide to a methylene group, yielding (N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)cyclohexane.
This sequence effectively utilizes the reduction of an amide with LiAlH₄ as the pivotal step to transform bromocyclohexane into (N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)cyclohexane.