The length of human pregnancies is approximately normal with mean p=266 days and standard deviation o = (a) (3 points) What is the probability that a randomly selected pregnancy lasts less than 262 days? (b) (3 points) Suppose a random sample of 51 pregnancies is obtained. Describe the sampling distribution of the sample mean length of pregnancies. (c) (3 points) What is the probability that a random sample of 51 pregnancies has a mean gestation period of 262 days or less? (d) (3 points) What is the probability that a random sample of 106 pregnancies has a mean gestation period of 262 days or less? (e) (3 points) What effect does increasing the sample size have on the probability? Provide an explanation for this result.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Let’s break down each part of the problem, step by step, and provide the necessary calculations along with explanations:
(a) Probability that a randomly selected pregnancy lasts less than 262 days
Given that human pregnancies are normally distributed with a mean ((\mu)) of 266 days and a standard deviation ((\sigma)) of 3 days, we are tasked with finding the probability that a pregnancy lasts less than 262 days.
To find the probability, we will use the Z-score formula:
[
Z = \frac{X – \mu}{\sigma}
]
Where:
- (X = 262) days (the value we’re interested in)
- (\mu = 266) days (mean of the distribution)
- (\sigma = 3) days (standard deviation)
First, we calculate the Z-score:
[
Z = \frac{262 – 266}{3} = \frac{-4}{3} = -1.33
]
Next, we look up the Z-score of (-1.33) in the standard normal distribution table (or use a calculator). This gives us the cumulative probability of a pregnancy lasting less than 262 days.
[
P(X < 262) = P(Z < -1.33) \approx 0.0918
]
So, the probability that a randomly selected pregnancy lasts less than 262 days is approximately 0.0918 or 9.18%.
(b) Sampling distribution of the sample mean for a sample of 51 pregnancies
When we take a random sample of size (n = 51), the sampling distribution of the sample mean is also normally distributed (thanks to the Central Limit Theorem). The mean of the sampling distribution is the same as the population mean, and the standard error (SE) is given by:
[
SE = \frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}} = \frac{3}{\sqrt{51}} \approx 0.421
]
Thus, the sampling distribution of the sample mean will have:
- Mean = 266 days
- Standard error = 0.421 days
(c) Probability that a sample of 51 pregnancies has a mean gestation period of 262 days or less
Now we are asked to find the probability that the sample mean of 51 pregnancies is 262 days or less. We can standardize this using the Z-score formula for the sample mean:
[
Z = \frac{\bar{X} – \mu}{SE}
]
Where:
- (\bar{X} = 262) days
- (\mu = 266) days
- (SE = 0.421)
Calculating the Z-score:
[
Z = \frac{262 – 266}{0.421} = \frac{-4}{0.421} \approx -9.49
]
The Z-score of (-9.49) is extremely far left on the normal distribution, so the cumulative probability associated with this Z-score is essentially 0. Therefore, the probability that the sample mean is 262 days or less is effectively 0.
(d) Probability that a sample of 106 pregnancies has a mean gestation period of 262 days or less
For a sample of 106 pregnancies, the standard error becomes:
[
SE = \frac{3}{\sqrt{106}} \approx 0.293
]
Now we calculate the Z-score for a sample mean of 262 days:
[
Z = \frac{262 – 266}{0.293} = \frac{-4}{0.293} \approx -13.65
]
This Z-score is even further to the left than in part (c), making the cumulative probability essentially 0 as well.
(e) Effect of increasing the sample size
Increasing the sample size reduces the standard error ((SE)) because (SE = \frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}). As the sample size increases, the standard error decreases, which makes the sampling distribution of the sample mean narrower and more concentrated around the population mean. This results in a decrease in the probability of observing extreme values (such as a sample mean of 262 days). In other words, as the sample size increases, the probability of obtaining a sample mean far from the population mean (266 days) becomes smaller.
Summary Explanation
- In part (a), we found the probability that a randomly selected pregnancy lasts less than 262 days using the Z-score formula and found it to be about 9.18%.
- In part (b), we explained the sampling distribution of the sample mean for a sample size of 51, which is normally distributed with a mean of 266 days and a standard error of 0.421 days.
- In part (c), we calculated the probability for a sample of 51 pregnancies to have a mean gestation period of 262 days or less, which was essentially 0 because the Z-score was extremely negative.
- In part (d), we found that for a sample of 106 pregnancies, the probability was also essentially 0 for the same reason.
- Finally, in part (e), we discussed how increasing the sample size reduces the standard error, making the sample mean more likely to be closer to the population mean and less likely to be extreme.
Let’s now visualize the distribution of sample means for different sample sizes to make these concepts clearer.
I’ll provide a graph to show the difference in the distribution of the sample mean for sample sizes of 51 and 106.
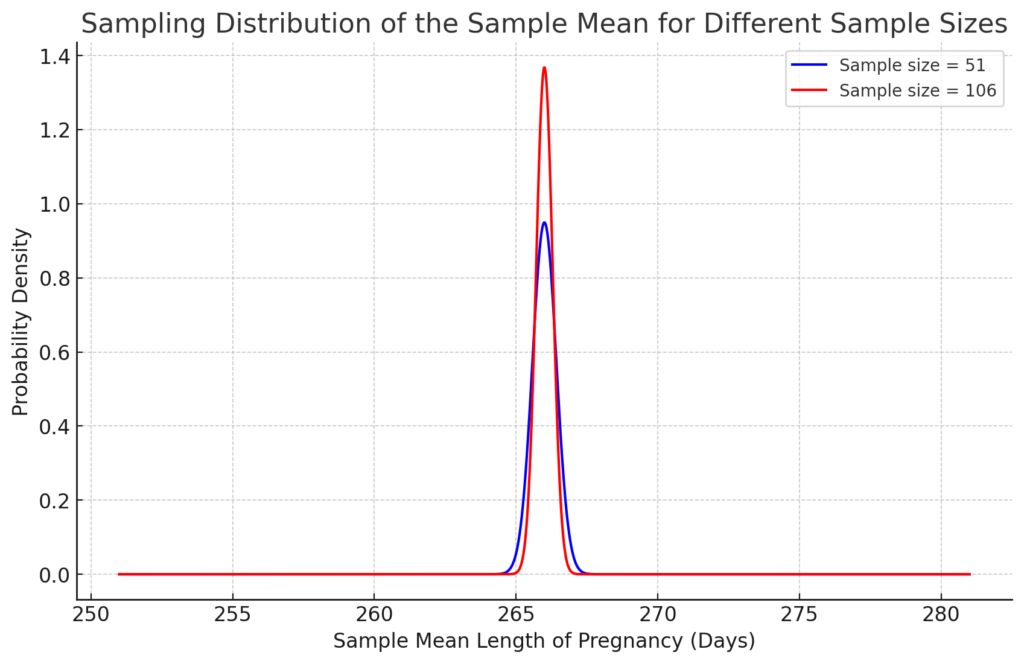
The graph above illustrates the sampling distribution of the sample mean for two different sample sizes: 51 and 106. As you can see, with the larger sample size (106), the distribution of the sample mean is much narrower and more concentrated around the population mean of 266 days, compared to the distribution for the smaller sample size (51). This shows how increasing the sample size reduces the standard error and makes the sample mean more likely to be closer to the population mean.
This result explains why, in part (e), increasing the sample size reduces the probability of obtaining extreme values like a sample mean of 262 days. As the sample size increases, the distribution becomes more concentrated, and the probability of seeing values far from the mean becomes very small.