Experts categorize problems based on
how similar the objects in the problem are.
surface and deep structures.
event-specific knowledge.
general principles that problems share.
The correct answer and explanation is:
iturn0image1turn0image8turn0image9turn0image10Experts categorize problems based on surface and deep structures. This approach allows them to identify underlying principles that govern problem-solving strategies, leading to more effective and efficient solutions.
Understanding Surface and Deep Structures
In problem-solving, two primary levels of analysis are recognized:
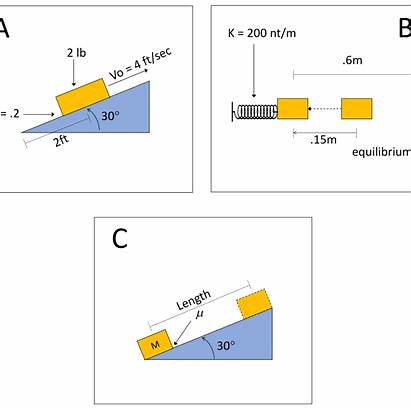
- Surface Structures: These pertain to the immediate, observable features of a problem, such as specific objects, contexts, or superficial details. For instance, in physics, surface features might include the presence of inclined planes, pulleys, or specific numerical values.
- Deep Structures: These involve the underlying principles, concepts, or laws that govern the problem’s framework. Continuing with the physics example, deep structures would encompass fundamental laws like Newton’s laws of motion or conservation principles.
Expert vs. Novice Problem Categorization
Research has demonstrated notable differences in how experts and novices approach problem categorization:
- Novices: Tend to categorize problems based on surface features. For example, they might group together all problems that mention inclined planes, regardless of the underlying physics principles involved. This approach often leads to challenges in applying appropriate solution strategies, as it overlooks the core concepts that should guide problem-solving.
- Experts: Focus on deep structures, identifying the fundamental principles that apply to a problem. By recognizing that different problems may share the same underlying concept, experts can apply similar solution strategies across various contexts. This deep structural recognition enables more flexible and adaptive problem-solving.
Implications of Deep Structure Categorization
Categorizing problems based on deep structures offers several advantages:
- Transferability: Understanding core principles allows experts to transfer knowledge across different scenarios, enhancing their ability to tackle novel problems effectively.
- Efficiency: By focusing on fundamental concepts, experts can bypass extraneous details, streamlining the problem-solving process.
- Adaptability: Deep structural recognition equips experts to adapt their knowledge to new and diverse situations, fostering innovative solutions.
Supporting Research
Studies have highlighted these distinctions in problem categorization. For instance, research on analogical reasoning emphasizes that experts are adept at mapping deep relational structures between problems, facilitating effective problem-solving and learning. citeturn0search10
Conclusion
By categorizing problems based on deep structures, experts leverage a profound understanding of fundamental principles, enabling efficient, transferable, and adaptive problem-solving strategies. This approach contrasts with surface-level categorization, which often limits flexibility and effectiveness in addressing complex challenges.