1. SATA is being replaced by NVMe for SSDs. What technology did SATA replace for HDDs?
a) 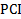
b) IDE
c) Firewire
d) USB
2. Which of these buses on a motherboard is the fastest?
a) USB 3.1
b) SATA III
c) PCle 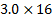
d) PCI Version 2.x
3. Typically, which dimension varies between sizes of M.2 SSD cards?
a) Width
b) Length
c) Height
d) Time (just kidding)
The correct answer and explanation is:
Answers:
- b) IDE
- c) PCIe
- b) Length
Explanation:
1. SATA replaced IDE for HDDs
SATA (Serial ATA) replaced IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics), also known as Parallel ATA (PATA), as the primary interface for hard drives. IDE was widely used in older computers and featured a bulky 40 or 80-wire ribbon cable, which limited airflow inside the computer case. SATA, introduced in the early 2000s, brought several improvements, including thinner cables, faster data transfer rates, and support for hot-swapping (removing and adding drives while the system is running). Over time, SATA evolved into SATA II and SATA III, offering speeds of up to 6 Gbps. However, with the rise of SSDs, SATA is being phased out in favor of NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express), which uses PCIe for significantly faster data speeds.
2. PCIe is the fastest bus on a motherboard
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) is the fastest interface available on modern motherboards, offering much higher bandwidth than other buses like USB 3.1, SATA III, or older PCI versions. PCIe operates in lanes (x1, x4, x8, x16), and each version improves data speeds. For example, PCIe 4.0 offers speeds up to 16 GT/s per lane, while PCIe 5.0 doubles that. High-performance devices such as GPUs, NVMe SSDs, and network adapters use PCIe for maximum speed.
3. M.2 SSD cards vary in length
M.2 SSDs come in different sizes, but their width is usually fixed at 22mm, while their length varies (e.g., 42mm, 60mm, 80mm, and 110mm). The length affects storage capacity, as longer M.2 SSDs can accommodate more NAND flash chips. Commonly, M.2 2280 (22mm x 80mm) is the standard for most consumer laptops and desktops.g