The adrenal medulla controls the short-term response to stress by
Group of answer choices
breaking down protein and fat.
reducing inflammation.
raising blood glucose levels.
suppressing immune cells.
increasing blood volume.
The correct answer and explanation is :
Correct Answer: Raising blood glucose levels.
The adrenal medulla plays a crucial role in the body’s short-term response to stress through the fight-or-flight mechanism. This is achieved by the release of catecholamines, primarily epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). These hormones are secreted rapidly in response to stressful stimuli, such as danger, excitement, or intense physical activity.
One of the major effects of adrenal medulla activation is raising blood glucose levels. This occurs through a process called glycogenolysis, where stored glycogen in the liver is broken down into glucose, providing immediate energy for muscles and vital organs. Epinephrine stimulates the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream, ensuring that cells have enough fuel to respond effectively to stress.
Other physiological effects of the adrenal medulla’s response to stress include:
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure, ensuring faster circulation of oxygen and nutrients.
- Bronchodilation (widening of airways), improving oxygen supply.
- Increased blood flow to muscles and brain, preparing the body for quick action.
- Suppression of non-essential functions, like digestion and reproductive activity, to focus energy on immediate survival.
While the adrenal cortex regulates long-term stress responses by releasing glucocorticoids like cortisol, the adrenal medulla is responsible for the immediate, short-term stress response. This rapid response is essential for survival, allowing an organism to either fight or flee from a perceived threat.
In summary, the correct answer is “raising blood glucose levels,” as the adrenal medulla helps mobilize energy quickly to respond to stressful situations.
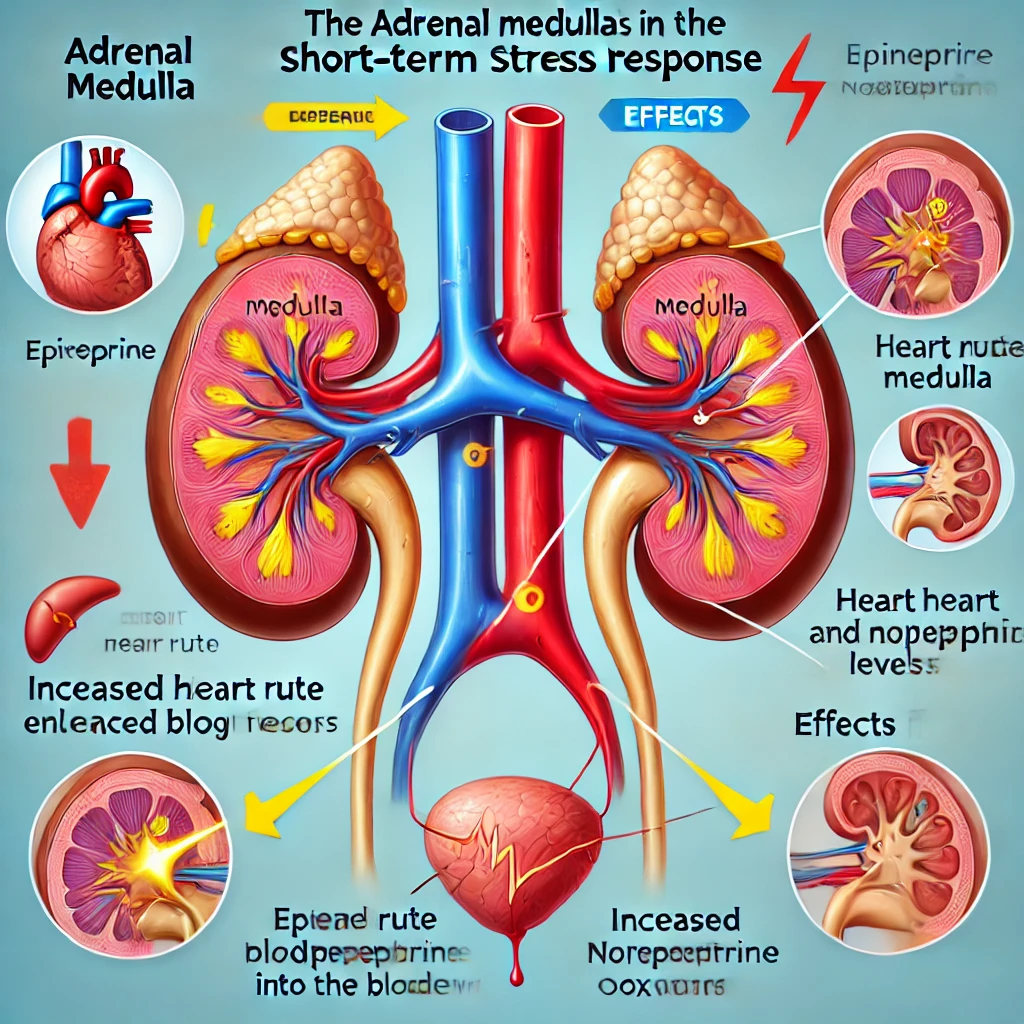
Here is an educational diagram illustrating the adrenal medulla’s role in the short-term stress response. It highlights the adrenal glands, the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine, and their effects on the body, such as increased heart rate and elevated blood glucose levels.