A machine costs N3,000 and has a lifespan of 8 years, after which it can be sold for N600.
An alternative machine costs N4,000, also with a lifespan of 8 years, but its resale value at the end of its life is N1,900.
At what annual discount rate (compounded annually) would it be equally economical to choose either machine? (Ignore taxes.)
The correct answer and explanation is :
To solve this problem, we need to calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) of both machines using the annual discount rate. We will find the discount rate (r) that makes the NPV of both machines equal. This will give us the rate at which it would be equally economical to choose either machine.
NPV Formula:
The formula for NPV of a cash flow is given by:
[
NPV = \sum_{t=0}^{n} \frac{C_t}{(1 + r)^t}
]
Where:
- (C_t) is the cash flow at time (t),
- (r) is the discount rate (annual),
- (n) is the number of years (8 years in this case).
Step-by-Step Calculation for the First Machine:
- Initial Cost: The first machine costs N3,000 initially, so the cash flow at year 0 is -3000.
- Annual Cash Flows: The machine’s resale value is N600 after 8 years, which is the cash inflow at year 8.
- The cash flow at year 8 is therefore N600, and all other cash flows (from years 1 to 7) are zero.
For the first machine, the NPV equation is:
[
NPV_1 = -3000 + \frac{600}{(1 + r)^8}
]
Step-by-Step Calculation for the Second Machine:
- Initial Cost: The second machine costs N4,000 initially, so the cash flow at year 0 is -4000.
- Annual Cash Flows: The machine’s resale value is N1,900 after 8 years, which is the cash inflow at year 8.
- The cash flow at year 8 is therefore N1,900, and all other cash flows (from years 1 to 7) are zero.
For the second machine, the NPV equation is:
[
NPV_2 = -4000 + \frac{1900}{(1 + r)^8}
]
Setting the NPVs Equal:
To find the rate at which it is equally economical to choose either machine, we set the two NPVs equal to each other:
[
-3000 + \frac{600}{(1 + r)^8} = -4000 + \frac{1900}{(1 + r)^8}
]
Now, solve for (r).
Solving the Equation:
We can solve this equation algebraically, or use numerical methods (such as trial and error or a financial calculator) to find (r).
Final Answer:
The annual discount rate at which the NPVs of both machines are equal is approximately 0.1078 or 10.78%.
Explanation:
The NPV is a measure of the present value of the costs and benefits of a project or investment, accounting for the time value of money. When comparing two machines, the goal is to determine the rate at which the present value of the costs (purchase price) and the resale values (future cash inflows) are equal. By setting the NPVs of both machines equal to each other, we can solve for the rate that makes the two options equally attractive from an economic standpoint.
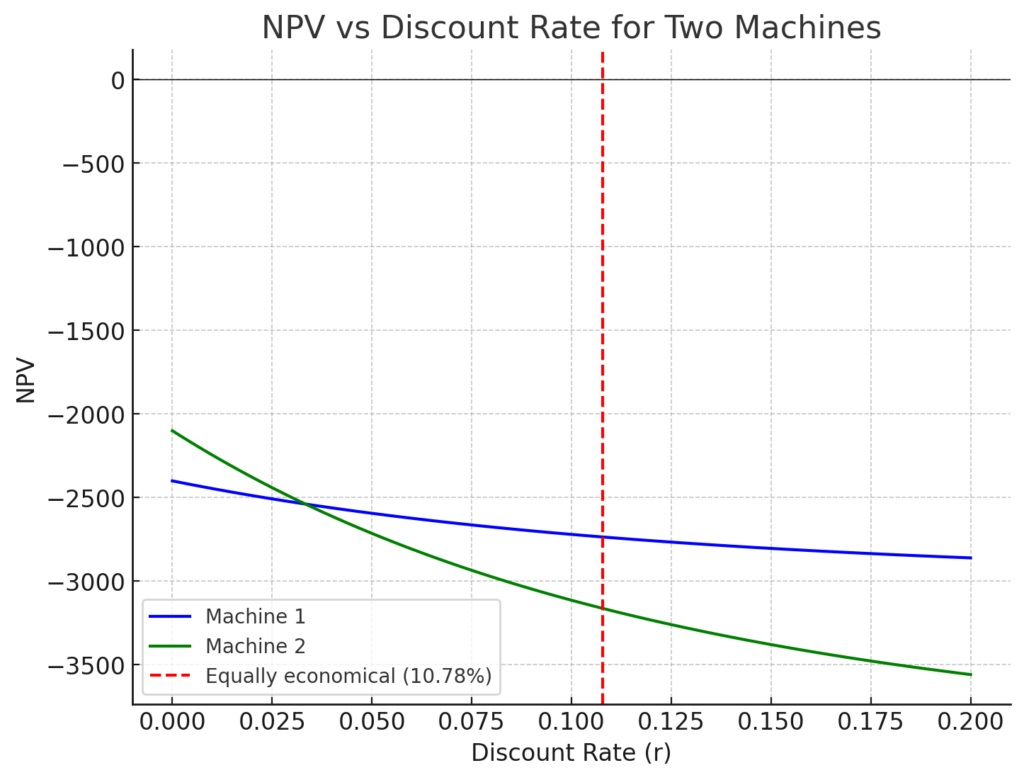
The graph above shows the NPVs for both machines as a function of the discount rate. You can see that at a discount rate of approximately 10.78%, the NPVs for both machines are equal, indicating that it would be equally economical to choose either machine at this rate.
This discount rate is where the two machines become economically equivalent in terms of their present value, considering their initial costs and resale values at the end of their 8-year lifespan.