Where is the DNA normally found in the cell?
The correct answer and explanation is :
The DNA in a cell is primarily found in two locations: the nucleus and the mitochondria.
1. Nucleus:
The nucleus is the central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, and it houses most of the cell’s genetic material in the form of chromosomes. Chromosomes are long strands of DNA wrapped around histone proteins. The nucleus acts as the control center for cellular activities such as growth, metabolism, protein synthesis, and cell division, with DNA serving as the blueprint for these functions. In the nucleus, DNA is organized into tightly coiled structures called chromatin, which condense into visible chromosomes during cell division.
The DNA in the nucleus contains the genetic instructions for making proteins and other molecules essential for the cell’s survival. The process of gene expression, where information in DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) and then translated into proteins, primarily occurs in the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
2. Mitochondria:
Mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell, also contain their own small amount of DNA, called mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). This DNA is inherited maternally and is separate from the nuclear DNA. Mitochondrial DNA plays a crucial role in the production of proteins involved in the process of cellular respiration, which generates energy in the form of ATP. Though mitochondrial DNA is much smaller than nuclear DNA, it is essential for the proper functioning of the mitochondria and energy production within the cell.
Explanation:
DNA is the molecular blueprint that carries the information necessary for the structure, function, and regulation of the cell. In eukaryotic cells, the nuclear DNA controls most of the cell’s activities, while mitochondrial DNA is crucial for energy production. Understanding the two locations of DNA is important for appreciating how genetic information is stored, accessed, and utilized within the cell.
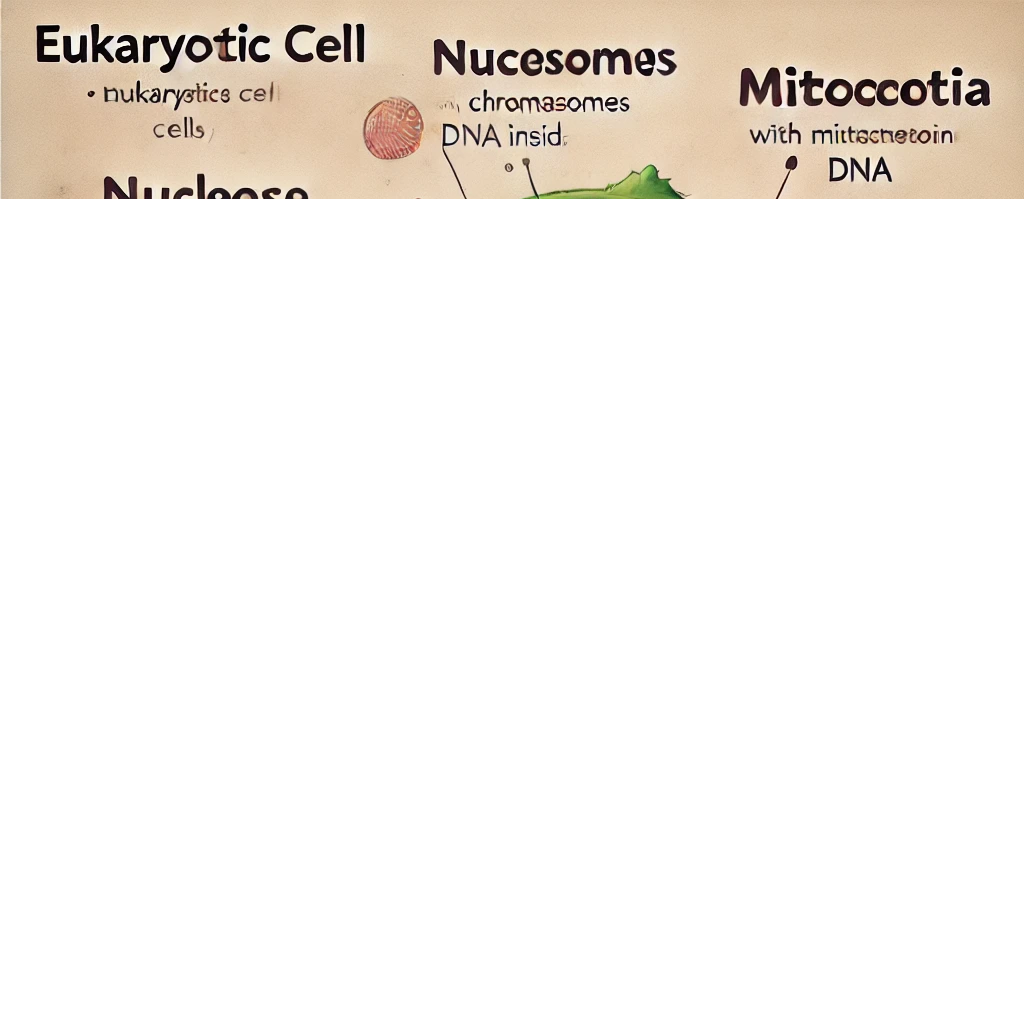
Here is an educational diagram showing the locations of DNA in the nucleus and mitochondria of a eukaryotic cell. As depicted, the nucleus contains the majority of the cell’s DNA, organized into chromosomes, while the mitochondria also contain a small amount of DNA, known as mitochondrial DNA. This diagram helps to visually understand where DNA is found within a cell.