Will a red blood cell undergo crenation, hemolysis, or no change in each of the following solutions? a. 1% (m/v) glucose b. 2% (m/v) NaCl c. 5% (m/v) glucose d. 0.1% (m/v) NaCl
The correct answer and explanation is :
Answer:
A red blood cell’s response to different solutions depends on the tonicity of the solution compared to the cell’s internal environment.
Effects of Each Solution:
- 1% (m/v) Glucose – No change
- This solution is isotonic to red blood cells because the physiological concentration of glucose in the blood is approximately 5% (m/v). A 1% glucose solution is close enough to isotonic conditions that it will not cause significant osmotic movement.
- 2% (m/v) NaCl – Crenation (shrinking)
- A 2% NaCl solution is hypertonic compared to the normal 0.9% NaCl in blood plasma. Since the solution has a higher solute concentration, water will leave the red blood cells, causing them to shrink and develop a spiky appearance (crenation).
- 5% (m/v) Glucose – No change
- A 5% glucose solution is isotonic to red blood cells, meaning there is no net movement of water into or out of the cells. This maintains the normal shape and function of the red blood cells.
- 0.1% (m/v) NaCl – Hemolysis (swelling and bursting)
- A 0.1% NaCl solution is hypotonic compared to the normal 0.9% NaCl concentration in blood plasma. Water will move into the red blood cells, causing them to swell and potentially burst (hemolysis).
Explanation:
The behavior of red blood cells in different solutions is dictated by osmosis, where water moves from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
- Isotonic Solution (No Change): The solute concentration inside and outside the cell is the same, so there is no net movement of water.
- Hypertonic Solution (Crenation): The external solute concentration is higher than inside the cell, causing water to leave, leading to cell shrinkage.
- Hypotonic Solution (Hemolysis): The external solute concentration is lower than inside the cell, causing water to enter, which may lead to swelling and bursting.
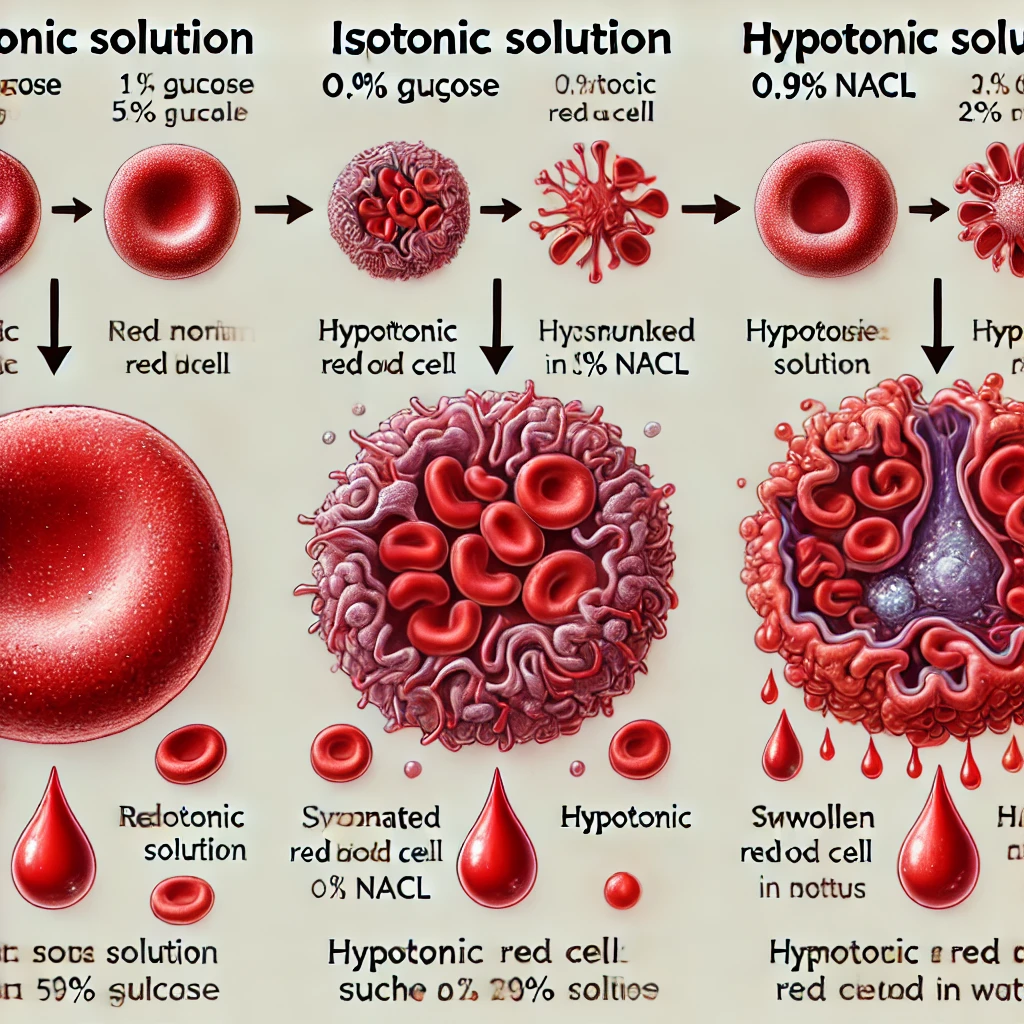
Here is an educational diagram illustrating the effects of different solutions on red blood cells. It visually represents isotonic, hypertonic (crenation), and hypotonic (hemolysis) conditions with labeled arrows indicating water movement.