Calculate the boiling point of a solution of 500.0 g of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) dissolved in 500.0 g of water. Kf = 1.86°C/m and Kb = 0.512°C/m. Use 100°C as the boiling point of
The correct answer and explanation is :
To calculate the boiling point of the solution, we need to apply the concept of boiling point elevation, which is the phenomenon where the boiling point of a solvent is raised when a non-volatile solute is added. The formula for boiling point elevation is:
[
\Delta T_b = K_b \times m
]
Where:
- (\Delta T_b) is the change in boiling point.
- (K_b) is the ebullioscopic constant (boiling point elevation constant) for the solvent, in this case, water.
- (m) is the molality of the solution.
Step 1: Calculate molality ((m))
Molality is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. First, we need to determine the number of moles of ethylene glycol (C₂H₆O₂).
- Molar mass of ethylene glycol (C₂H₆O₂):
- Carbon (C) has an atomic mass of 12.01 g/mol.
- Hydrogen (H) has an atomic mass of 1.008 g/mol.
- Oxygen (O) has an atomic mass of 16.00 g/mol.
Thus, the molar mass of C₂H₆O₂ is:
[
M_{\text{C}_2\text{H}_6\text{O}_2} = 2(12.01) + 6(1.008) + 2(16.00) = 62.068 \, \text{g/mol}
]
- Moles of ethylene glycol:
[
\text{moles of C}_2\text{H}_6\text{O}_2 = \frac{500.0 \, \text{g}}{62.068 \, \text{g/mol}} = 8.05 \, \text{mol}
]
- Molality ((m)):
Molality is the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. Since we have 500.0 g (0.5000 kg) of water:
[
m = \frac{\text{moles of C}_2\text{H}_6\text{O}_2}{\text{kg of solvent}} = \frac{8.05 \, \text{mol}}{0.5000 \, \text{kg}} = 16.10 \, \text{mol/kg}
]
Step 2: Calculate boiling point elevation ((\Delta T_b))
Now we can use the formula for boiling point elevation:
[
\Delta T_b = K_b \times m = 0.512 \, \text{°C/m} \times 16.10 \, \text{mol/kg} = 8.23 \, \text{°C}
]
Step 3: Determine the new boiling point
The normal boiling point of water is 100°C, so the new boiling point is:
[
\text{New boiling point} = 100°C + 8.23°C = 108.23°C
]
Conclusion:
The boiling point of the solution is 108.23°C.
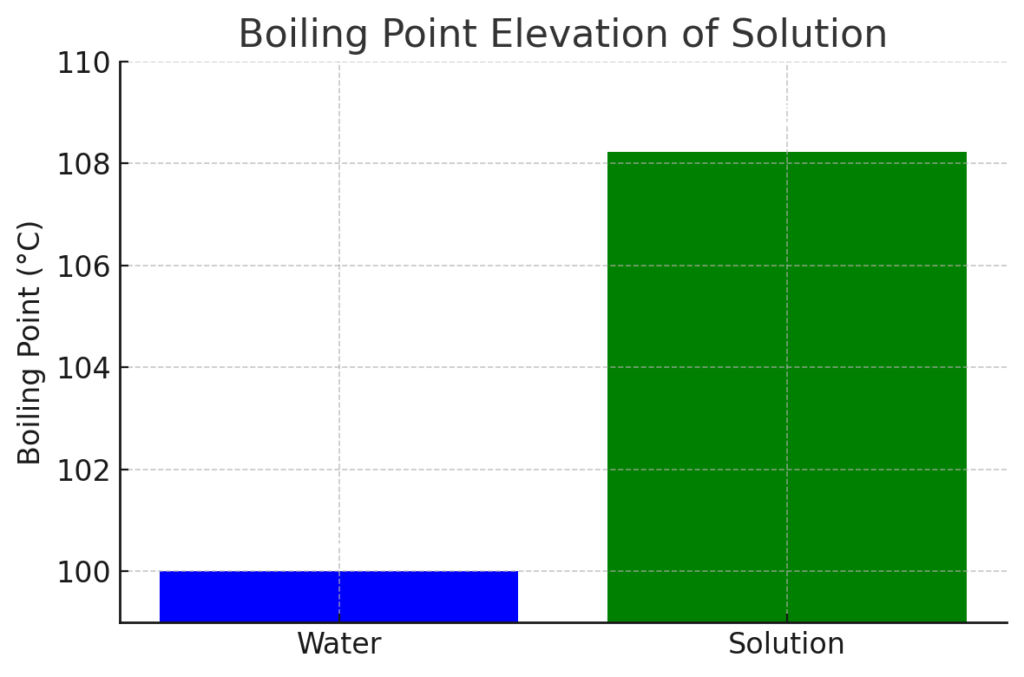
Here is the visual representation of the boiling point elevation. The bar on the left represents the boiling point of pure water (100°C), while the bar on the right represents the boiling point of the solution (108.23°C). The solution’s boiling point has increased due to the presence of ethylene glycol, as calculated earlier.