Which of the following is not a characteristic of a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium?
A) Marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
B) Price is equal to average revenue.
C) The firm has excess capacity.
D) Price is equal to marginal cost.
The correct answer and explanation is :
Correct Answer: D) Price is equal to marginal cost.
Explanation:
A monopolistically competitive firm operates in a market structure that has characteristics of both perfect competition and monopoly. In the long-run equilibrium, the firm produces where marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost (MC), but price (P) is greater than marginal cost (MC) due to product differentiation and market power.
Let’s analyze each option:
- Marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost (MR = MC) [Correct]
- Like all profit-maximizing firms, a monopolistically competitive firm sets output where MR = MC. This ensures the firm is producing the quantity that maximizes its profit or minimizes its losses.
- Price is equal to average revenue (P = AR) [Correct]
- In any market structure, price (P) is always equal to average revenue (AR) because AR is calculated as total revenue divided by quantity, which is simply the price.
- The firm has excess capacity [Correct]
- Unlike perfectly competitive firms, monopolistically competitive firms do not produce at the lowest point of their average total cost (ATC) curve. Instead, they operate at a lower output level, leading to excess capacity—a gap between the profit-maximizing quantity and the efficient scale of production.
- Price is equal to marginal cost (P = MC) [Incorrect]
- In perfect competition, P = MC, leading to allocative efficiency. However, in monopolistic competition, firms have some degree of market power, allowing them to charge a price greater than marginal cost (P > MC). This creates a deadweight loss, indicating some inefficiency in resource allocation.
Thus, option D is incorrect because in monopolistic competition, price exceeds marginal cost in long-run equilibrium.
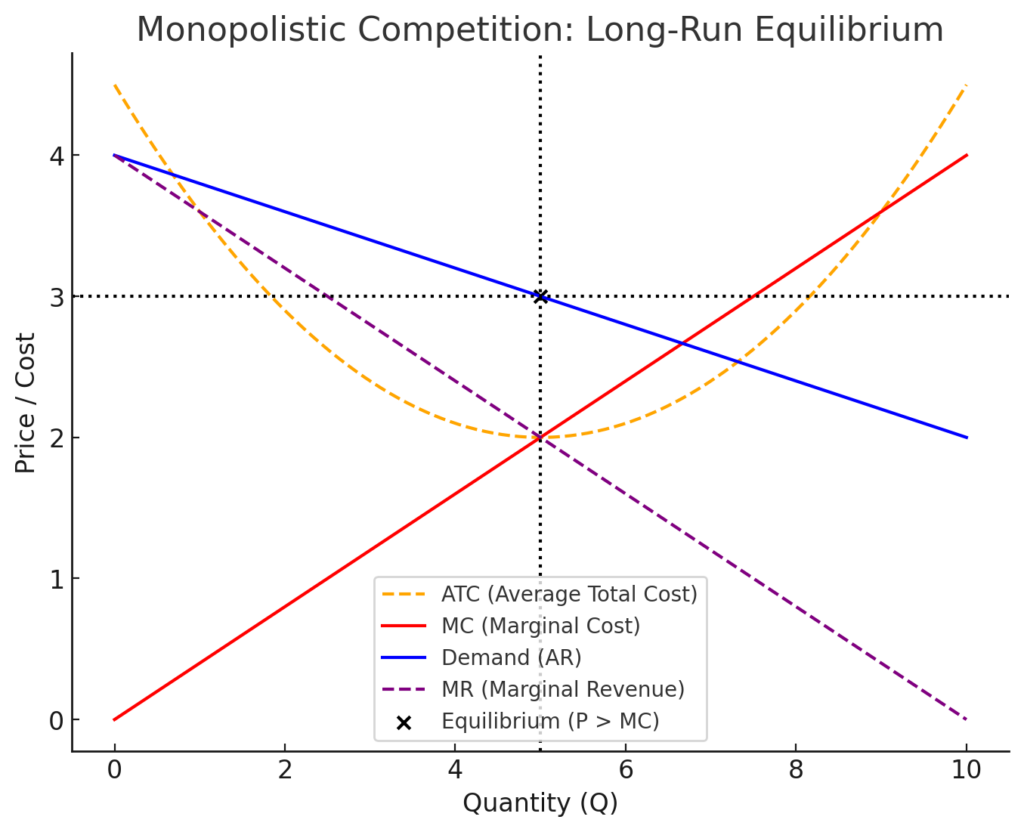
The graph above illustrates the long-run equilibrium of a monopolistically competitive firm. It shows that the firm sets MR = MC to maximize profit, but the price is greater than marginal cost (P > MC), confirming that option D is incorrect. Additionally, the firm does not produce at the lowest ATC, demonstrating excess capacity.