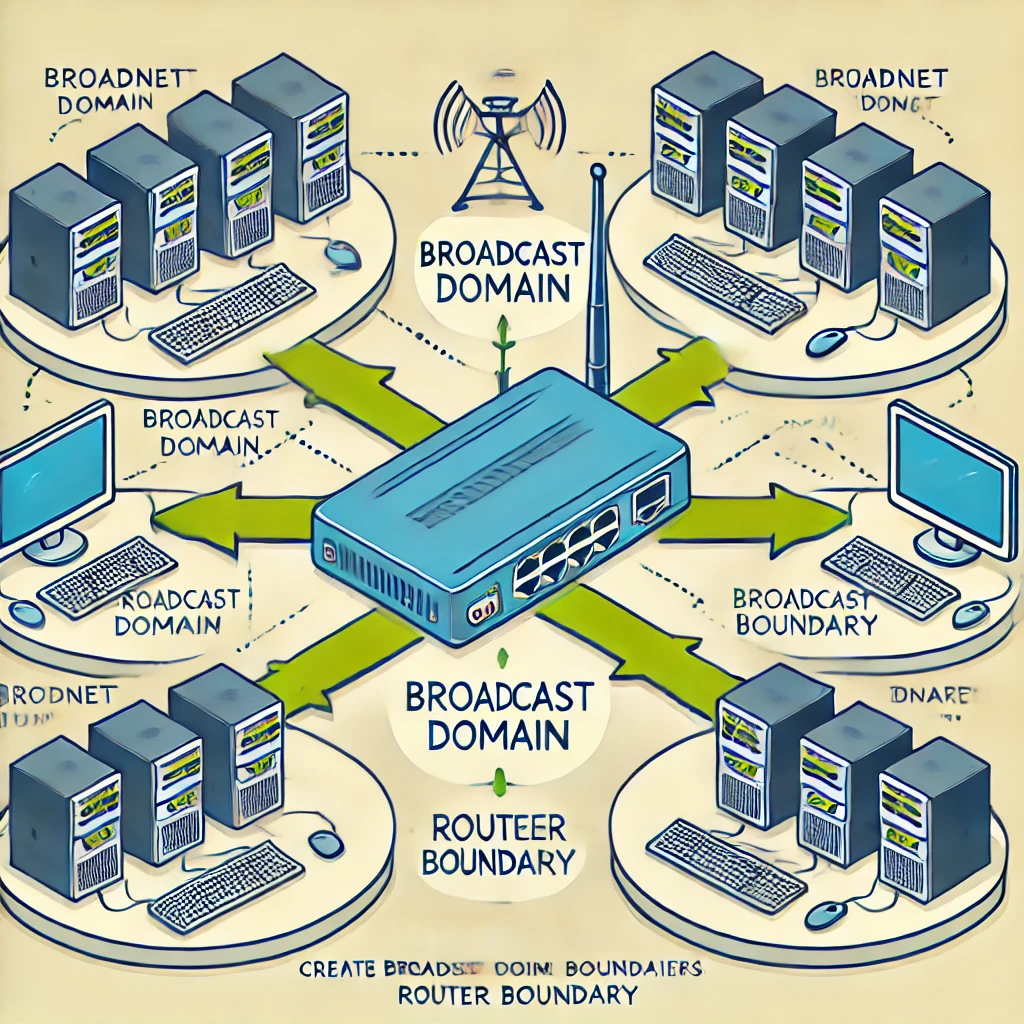
How do routers create a broadcast domain boundary?
a. They forward broadcasts only to necessary segments.
b. They listen to and direct broadcast traffic.
c. They only forward broadcasts that are intended for multiple subnets.
d. They do not forward broadcast traffic.
The correct answer and explanation is:
The correct answer is:
d. They do not forward broadcast traffic.
Explanation:
A broadcast domain is a network segment where a broadcast frame (a packet sent to all devices) can reach all connected devices without passing through a router. Broadcast traffic is used for various network discovery protocols, such as ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Routers play a critical role in creating broadcast domain boundaries because they do not forward broadcast traffic beyond the local network segment. This is one of the fundamental differences between routers and switches.
How Routers Create Broadcast Domain Boundaries
- Blocking Broadcast Packets:
- When a device in one subnet sends a broadcast message (e.g., ARP request), the router does not forward it to other subnets. This prevents unnecessary network congestion.
- Segmenting Networks:
- Each interface of a router connects to a different subnet, effectively creating separate broadcast domains. Devices within the same subnet can communicate using broadcasts, but communication between subnets requires routing.
- Enhancing Network Performance and Security:
- Since broadcast traffic is limited to its subnet, routers help reduce network congestion and prevent broadcast storms (where excessive broadcasts degrade network performance).
- This also improves security by limiting network-wide exposure of certain types of traffic.
- Using Unicast and Multicast Instead:
- If inter-subnet communication is needed, routers use unicast (one-to-one) or multicast (one-to-many specific devices) instead of broadcasting.
Comparison with Switches and Hubs
- Hubs forward broadcasts to all devices (one large broadcast domain).
- Switches break up collision domains but still allow broadcasts within a VLAN.
- Routers create broadcast domain boundaries, ensuring better network segmentation and efficiency.
By preventing broadcast traffic from spreading beyond a subnet, routers maintain efficient, scalable, and secure networks.
Now, I’ll generate an image to illustrate this concept.
I’ve created an image illustrating how routers create broadcast domain boundaries. It visually represents multiple subnets connected to a central router, with broadcast traffic contained within each subnet. Let me know if you need any modifications or further explanations!