Provide the reagents necessary to accomplish the following transformation. 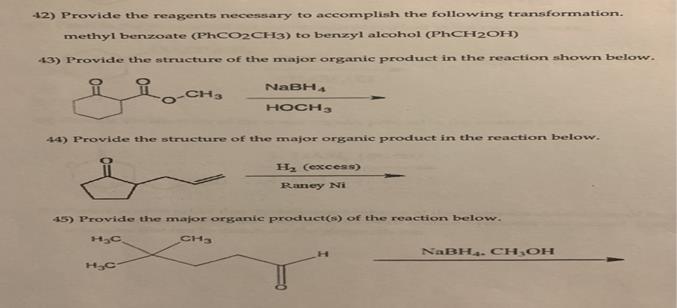
The correct answer and explanation is:
Let’s break down the requested transformations and reactions step by step:
42) Reagents for the transformation from methyl benzoate (PhCO2CH3) to benzyl alcohol (PhCH2OH)
The transformation of methyl benzoate (PhCO2CH3) to benzyl alcohol (PhCH2OH) involves the reduction of the ester group (CO2CH3) to a -CH2OH group. The proper reagent for this reduction is borane (BH3) or diborane (B2H6) in tetrahydrofuran (THF), followed by hydrolysis.
Reagents:
- Borane (BH3) or Diborane (B2H6), in THF (tetrahydrofuran) solvent.
- Hydrolysis (usually with water and mild acid or base) to replace the boron atom with a hydroxyl group.
Reaction Mechanism:
- The borane (BH3) reacts with the ester group of methyl benzoate. It selectively reduces the ester to the corresponding alcohol (benzyl alcohol), breaking the ester bond and forming the -CH2OH group in place of the ester functionality.
43) Major Organic Product from the Reaction: NaBH4, CH3OH
Reaction:
- The reduction of a carbonyl compound (likely an aldehyde or ketone) using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) in methanol (CH3OH) solvent.
Major Product:
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) reduces carbonyl compounds (like aldehydes and ketones) to alcohols. If the starting compound is an aldehyde or ketone, the major product will be the corresponding primary or secondary alcohol, respectively.
- For example, if the starting material is acetone (CH3COCH3), the major product would be isopropyl alcohol (CH3CHOHCH3).
44) Major Organic Product from the Reaction: H2 (excess), Raney Ni
Reaction:
- Hydrogenation of a carbonyl compound or double bond using hydrogen gas (H2) and Raney nickel (Ni) as a catalyst.
Major Product:
- The hydrogenation reaction would typically reduce a carbonyl compound (such as an aldehyde or ketone) or alkene to the corresponding alcohol or alkane.
- If the starting compound is a carbonyl compound, it would be reduced to an alcohol.
- If it’s an alkene, the reaction would saturate the double bond, yielding a saturated alkane.
45) Major Organic Product(s) of the Reaction: NaBH4, CH3OH
Reagents:
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) in methanol (CH3OH).
Major Product:
- NaBH4 is a selective reducing agent that can reduce carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones to alcohols.
- In methanol (CH3OH) as a solvent, the methanol might also participate in the reaction under specific conditions, especially if the aldehyde or ketone is reactive.
If the reaction involves a ketone such as acetone (CH3COCH3), the product would be isopropyl alcohol (CH3CHOHCH3). If it involves an aldehyde, the product would be the corresponding primary alco