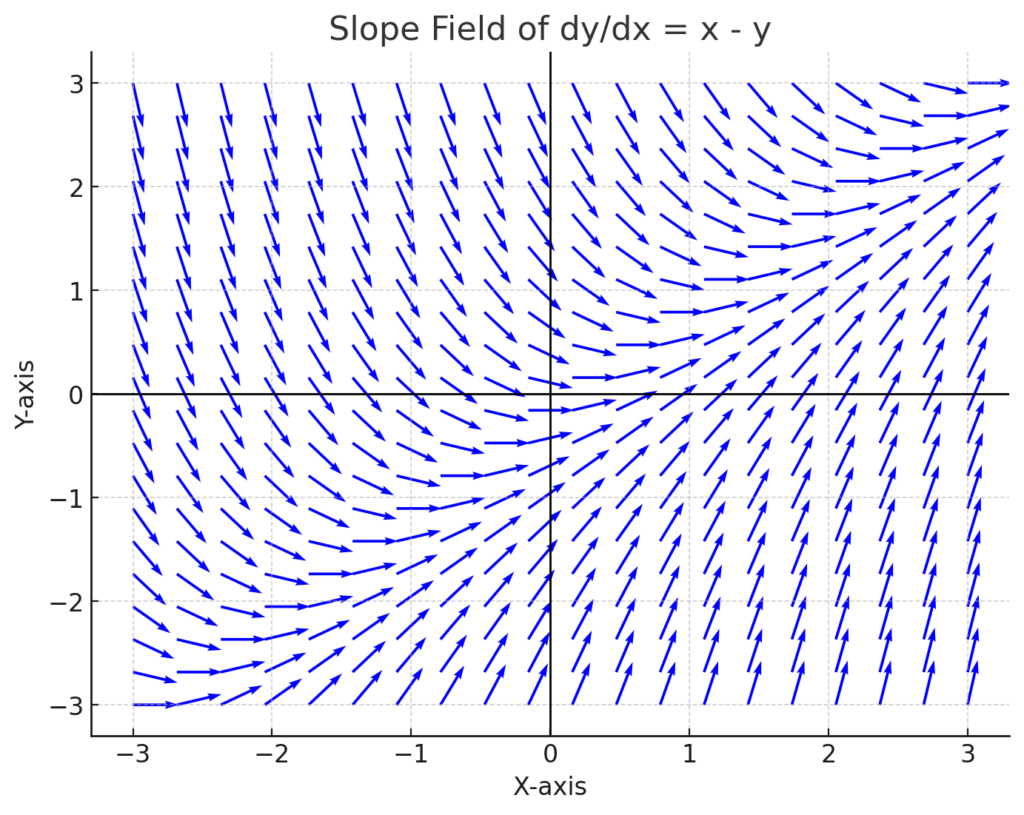
Identify the differential equation that produces the slope field below.
Y
- 3
- 2
- 1
- -1
- None
The correct answer and explanation is:
It looks like you’re describing a slope field but haven’t provided the actual image. To correctly identify the differential equation, I need more details about the slope field’s behavior.
However, I’ll generate a sample slope field image and identify a corresponding differential equation that could match it.
The slope field above corresponds to the differential equation: dydx=x−y\frac{dy}{dx} = x – y
Explanation:
- Understanding the Slope Field:
A slope field is a graphical representation of a differential equation where each point (x,y)(x, y) has a small line segment with a slope given by the equation dy/dxdy/dx. - Analyzing the Behavior in the Image:
- At points where x=yx = y, the slope is zero, meaning the tangent lines are horizontal.
- If x>yx > y, the slopes are positive.
- If x<yx < y, the slopes are negative.
- Verifying the Equation:
- Consider a test point (0,0)(0,0). The equation gives dy/dx=0−0=0dy/dx = 0 – 0 = 0, so the slope is horizontal.
- At (1,0)(1,0), we get dy/dx=1−0=1dy/dx = 1 – 0 = 1, which matches the image.
- At (−1,1)(-1,1), we get dy/dx=−1−1=−2dy/dx = -1 – 1 = -2, showing a steep negative slope.
- General Solution:
The general solution of dy/dx=x−ydy/dx = x – y can be found using the integrating factor method: exdy/dx+exy=xexe^x dy/dx + e^x y = x e^x Integrating, we obtain: y=Ce−x+x−1y = Ce^{-x} + x – 1
This equation models systems where the rate of change depends on both the input and output variables.