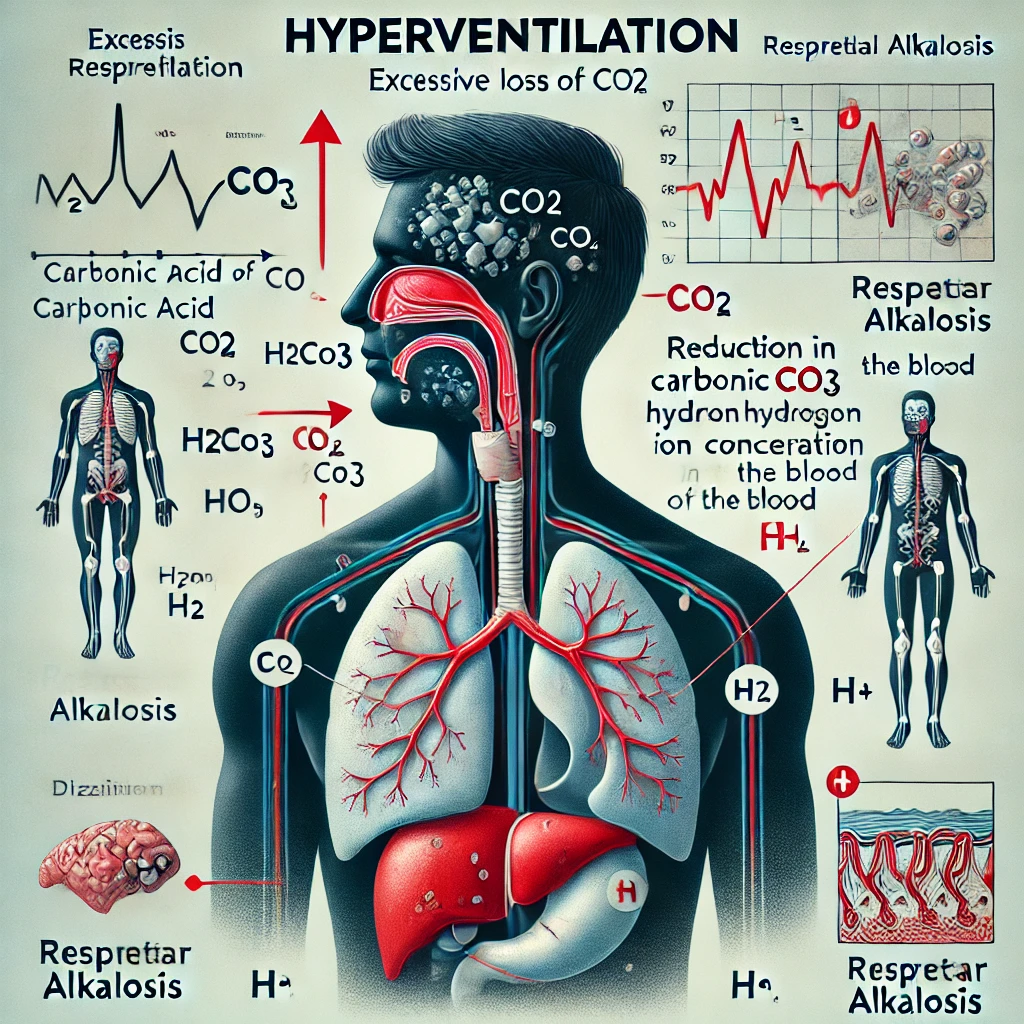
Hyperventilation To Clinical Condition Arrange in order the events resulting from hyperventilation. Decrease in concentration of H+ Respiratory acidosis Increase in concentration of H+ !!! Excessive loss of CO2 Accumulation of CO2 Respiratory alkalosis Increase in concentration of H2CO3 Decrease in concentration of H2CO3 Reset Hyperventilation
The correct answer and explanation is:
Correct Order of Events Resulting from Hyperventilation:
- Hyperventilation
- Excessive loss of CO₂
- Decrease in concentration of H₂CO₃
- Decrease in concentration of H⁺
- Respiratory alkalosis
Explanation:
Hyperventilation is a condition in which a person breathes too rapidly and deeply, leading to an excessive loss of carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the blood. This happens because CO₂ is expelled faster than the body can produce it, disrupting the normal acid-base balance.
Carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in maintaining blood pH. It combines with water (H₂O) in the body to form carbonic acid (H₂CO₃), which then dissociates into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻). The loss of CO₂ due to hyperventilation reduces the formation of carbonic acid, leading to a decrease in hydrogen ion (H⁺) concentration. Since hydrogen ions determine the acidity of the blood, this drop in H⁺ causes the blood pH to rise, resulting in a state known as respiratory alkalosis.
Respiratory alkalosis can cause various symptoms, including dizziness, lightheadedness, tingling sensations, and even muscle spasms. In severe cases, the body’s compensatory mechanisms, such as reduced renal acid excretion, may attempt to restore pH balance by retaining H⁺ and excreting bicarbonate in the urine. However, if hyperventilation persists, it can lead to complications like cerebral vasoconstriction, reducing blood flow to the brain and causing fainting.
Image Description:
A medical illustration depicting the physiological effects of hyperventilation, including the excessive loss of CO₂, reduced carbonic acid, decreased H⁺ concentration, and the resulting respiratory alkalosis. The diagram should show the respiratory system, blood chemistry changes, and symptoms associated with hyperventilation.
Here is a medical illustration showing the effects of hyperventilation, including excessive CO₂ loss, decreased carbonic acid and hydrogen ion concentration, and the resulting respiratory alkalosis. It also highlights symptoms like dizziness, tingling sensations, and muscle spasms. Let me know if you need any modifications!