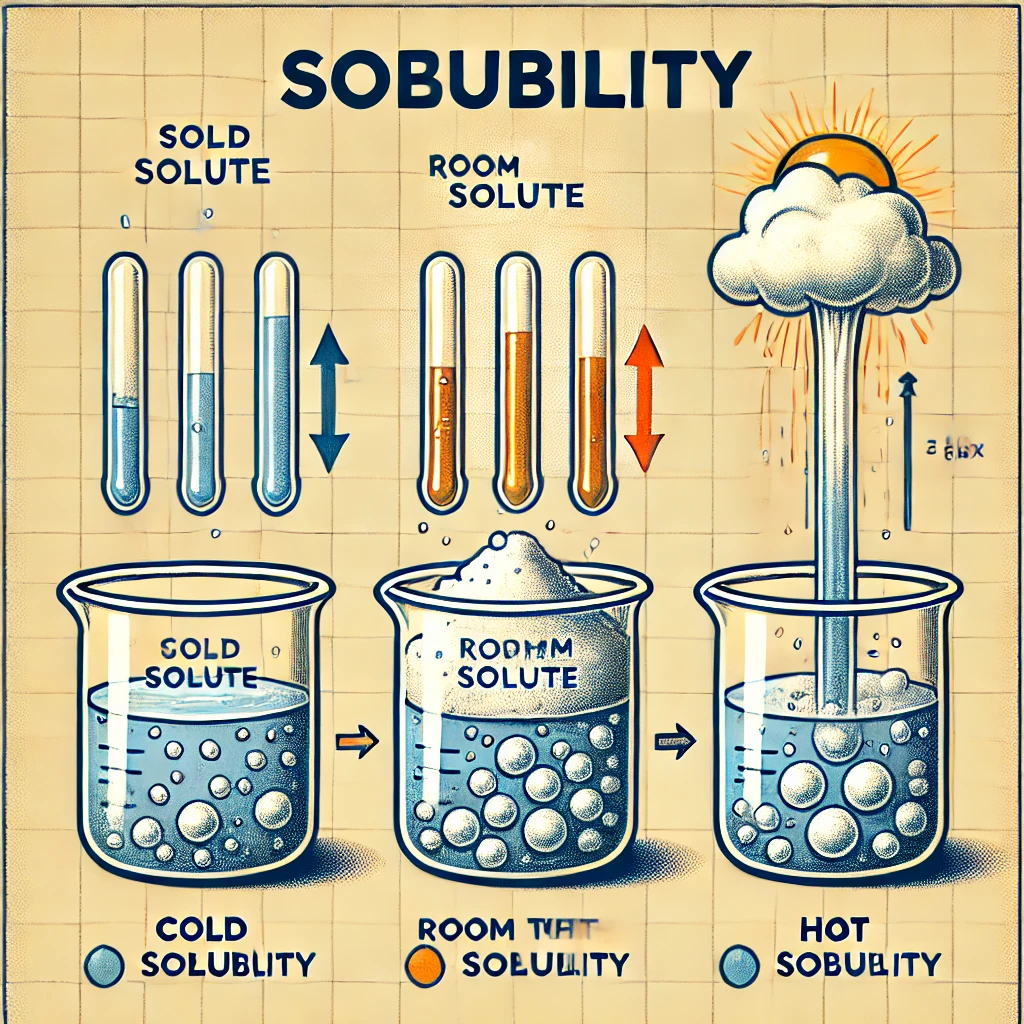
An increase in the temperature of a solution usually:
A decreases the solubility of a solid solute in the solution
B increases the solubility of a solid solute in the solution
C increases the boiling point of the solution
D decreases the solubility of a liquid solute in the solution
E increases the solubility of a gas in the solution
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct answer is:
B) Increases the solubility of a solid solute in the solution.
Explanation:
Solubility refers to the ability of a solute to dissolve in a solvent. The effect of temperature on solubility depends on the nature of the solute—whether it is a solid, liquid, or gas.
For solid solutes, an increase in temperature typically increases solubility. This occurs because dissolving a solid in a liquid is often an endothermic process, meaning it absorbs heat. As temperature rises, more energy is available to break intermolecular bonds in the solid and allow solute particles to mix with the solvent. For example, sugar and salt dissolve better in hot water than in cold water.
For gaseous solutes, an increase in temperature decreases solubility (eliminating option E). This happens because gases escape more easily from a liquid when heated, as higher temperatures give gas molecules more kinetic energy to overcome attractive forces and leave the solution. This principle explains why carbonated beverages lose their fizz faster in warm conditions.
For liquid solutes, temperature effects vary, but generally, their solubility does not follow a strict pattern (making option D incorrect).
Additionally, while temperature increases the boiling point of a solution due to vapor pressure changes, this does not directly relate to solubility (eliminating option C).
In summary, heating a solution typically enhances the solubility of solid solutes, making option B the correct answer.