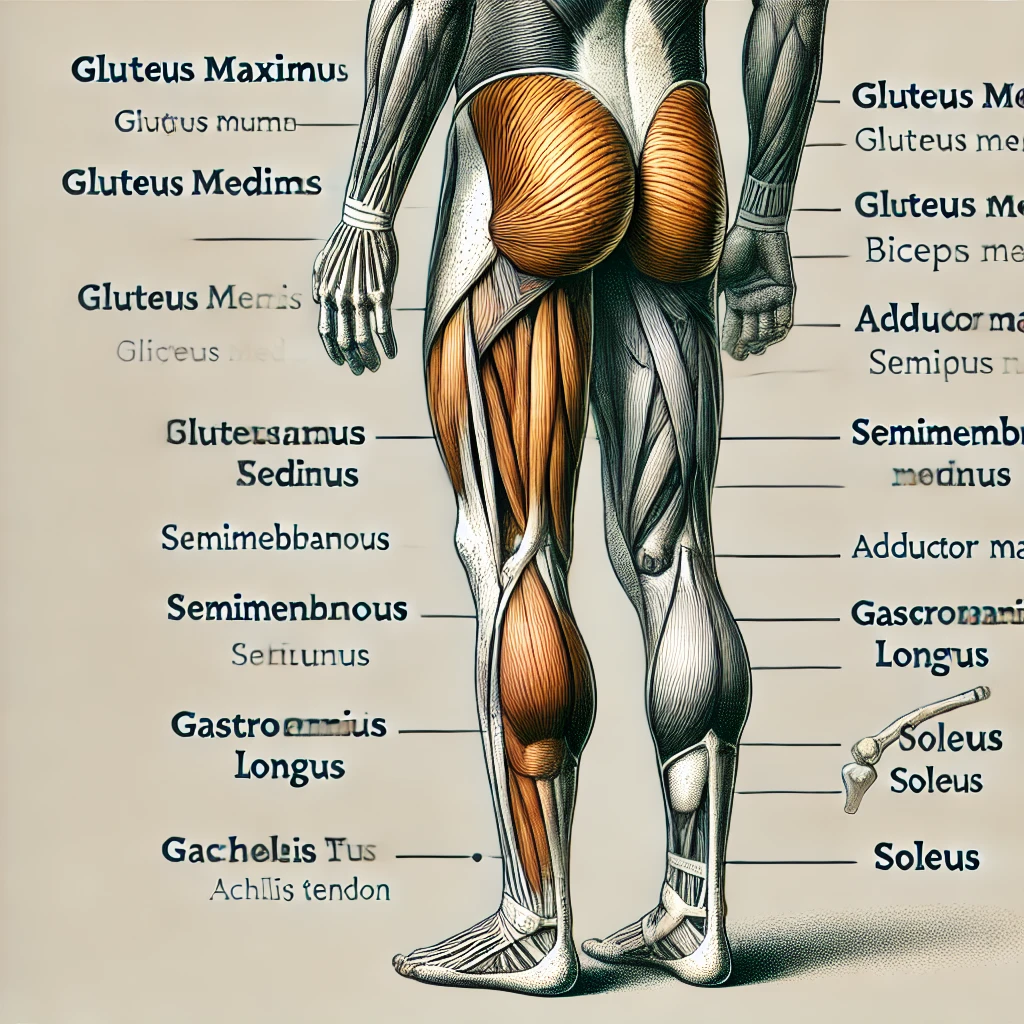
Art-Labeling Activity: Posterior muscles of the lower body Part A Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Reset Help
- Gluteus maximus
- Fibularis longus
- Semimembranosus
- Gluteus medius
- Biceps femoris
- Somitendinosus
- Gastrocnemius
- Calcanea (Achilles)
- Soleus
- Adductor magnus
The correct answer and explanation is:
Correct Answer for Labeling Posterior Muscles of the Lower Body:
- Gluteus maximus – Located in the upper buttock region, this large muscle is responsible for hip extension, outward rotation, and stability of the hip.
- Gluteus medius – Found on the outer surface of the pelvis, above the gluteus maximus, this muscle aids in hip abduction and stabilization.
- Biceps femoris – Part of the hamstrings group, it runs along the back of the thigh and is involved in knee flexion and hip extension.
- Semimembranosus – Another hamstring muscle, it is deeper than the biceps femoris and helps with knee flexion and hip extension.
- Semitendinosus – This muscle, alongside the semimembranosus, contributes to knee flexion and internal rotation of the tibia.
- Adductor magnus – Found on the inner thigh, this muscle assists with hip adduction and medial rotation.
- Fibularis longus – Located on the outer side of the lower leg, this muscle helps with plantarflexion and foot eversion.
- Gastrocnemius – A large, superficial calf muscle that plays a crucial role in plantarflexion of the foot and knee flexion.
- Soleus – Positioned beneath the gastrocnemius, it aids in plantarflexion and endurance-related standing postures.
- Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon – The thick tendon connecting the gastrocnemius and soleus to the calcaneus (heel bone), enabling strong push-off movements.
Explanation:
The posterior muscles of the lower body play a vital role in movement, stability, and power. The gluteal muscles contribute to hip function and locomotion. The hamstrings are essential for knee movement and balance, while the adductor magnus assists in leg control. The calf muscles, including the gastrocnemius and soleus, generate force for walking, running, and jumping. The Achilles tendon is crucial for transmitting power from the calf muscles to the foot. Together, these muscles support posture, movement, and athletic performance.