What part of a neuron contains the nucleus?
a. Dendrite.
b. Cell body (soma).
c. Axon.
d. Node of Ranvier.
The correct answer and explanation is :
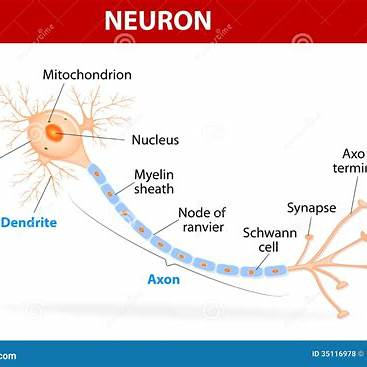
The correct answer is b. Cell body (soma).
Neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, are specialized cells responsible for transmitting information throughout the body. A typical neuron consists of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and an axon.
Cell Body (Soma): The soma is the central part of the neuron and contains the nucleus, which houses the cell’s genetic material. The nucleus plays a crucial role in regulating cellular functions and maintaining the neuron’s health. The soma also contains other organelles such as mitochondria, which provide energy, and ribosomes, which synthesize proteins necessary for the neuron’s function. The soma integrates incoming signals from the dendrites and determines whether to generate an electrical impulse.
Dendrites: These are tree-like extensions from the soma that receive chemical signals from other neurons. Dendrites convert these chemical signals into electrical impulses and transmit them toward the soma. The extensive branching of dendrites increases the neuron’s surface area, allowing it to form connections with numerous other neurons.
Axon: The axon is a long, slender projection that conducts electrical impulses away from the soma toward other neurons, muscles, or glands. Many axons are covered with a myelin sheath, a fatty layer that insulates the axon and accelerates the transmission of electrical signals. The axon terminates in axon terminals, which release neurotransmitters to communicate with target cells.
Node of Ranvier: These are small gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon. Nodes of Ranvier facilitate rapid conduction of nerve impulses by allowing the electrical signal to jump from one node to the next, a process known as saltatory conduction.
Understanding the structure of neurons is fundamental to comprehending how the nervous system functions, as the intricate design of each component plays a vital role in neural communication.