If an organism receives recombinant DNA by genetic engineering from the same species of organism, this animal is considered to be…
a. genetically modified organism
b. transgenic organism
c. transgenomic organism
d. None of these are true
The correct answer and explanation is :
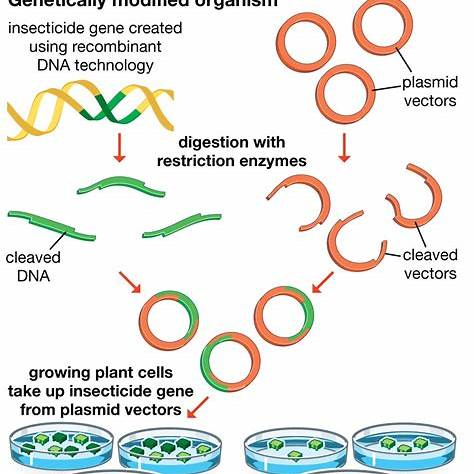
When an organism receives recombinant DNA from the same species through genetic engineering, it is classified as a genetically modified organism (GMO). The term “transgenic organism” specifically refers to organisms that have incorporated DNA from a different species. The term “transgenomic organism” is not commonly used in this context.
Understanding Genetic Modification Within the Same Species
Genetic modification involves altering an organism’s genome using biotechnology to introduce, remove, or modify specific genes. When the genetic material introduced comes from the same species, the organism is considered a GMO. This process can enhance desirable traits, such as disease resistance or increased productivity, without introducing foreign DNA.
Differentiating Between GMOs and Transgenic Organisms
While all transgenic organisms are GMOs, not all GMOs are transgenic. The distinction lies in the source of the genetic material:
- Genetically Modified Organism (GMO): An organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques, which can include the insertion, deletion, or modification of genes from the same species.
- Transgenic Organism: A subset of GMOs that contain genes inserted from a different species. This cross-species gene transfer can introduce new traits that are not naturally found in the recipient species.
Applications and Implications
Genetic modifications within the same species are often employed to enhance traits without crossing species barriers. For example, crops may be modified to improve yield or resistance to pests by altering their own genes. This approach can be more acceptable to the public and regulatory bodies, as it avoids the complexities associated with transgenic modifications.
In contrast, transgenic modifications allow for the introduction of novel traits by incorporating genes from different species. This has led to significant advancements in agriculture, medicine, and research but also raises ethical and ecological considerations.
Conclusion
In summary, when an organism receives recombinant DNA from the same species through genetic engineering, it is termed a genetically modified organism (GMO). The term “transgenic organism” is reserved for cases where the introduced genetic material originates from a different species. Understanding this distinction is crucial in discussions about genetic engineering and its applications.