The oxygen released by photosynthesis is produced by which of the following processes?
A) chemiosmosis
B) the electron transfer system of photosystem
C) splitting water molecules
D) the electron transfer system of photosystem II.
The correct answer and explanation is :
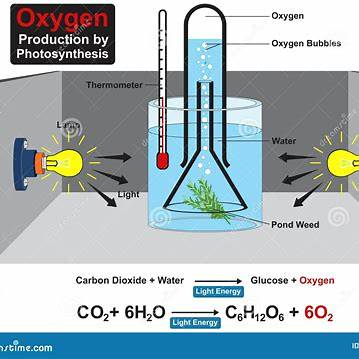
he correct answer is C) splitting water molecules.
In photosynthesis, the oxygen released into the atmosphere originates from the splitting of water molecules, a process known as photolysis. This critical reaction occurs within Photosystem II (PSII), the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. When photons of light are absorbed by PSII, their energy is used to extract electrons from water molecules. This extraction results in the production of electrons, protons (hydrogen ions), and molecular oxygen (O₂). The overall reaction can be summarized as:
[ 2H₂O → 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ + O₂ ]
The electrons generated are transferred through a series of proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane, known as the electron transport chain. This transfer facilitates the formation of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane, which is then utilized by ATP synthase to produce ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell. Additionally, these electrons reduce NADP⁺ to NADPH, a molecule that provides reducing power for the Calvin cycle, where carbon fixation occurs.
The protons released into the thylakoid lumen contribute to the proton gradient essential for ATP synthesis. Meanwhile, the molecular oxygen produced as a by-product diffuses out of the chloroplast and is released into the atmosphere, contributing to the Earth’s oxygen supply.
This understanding was first elucidated through experiments by Cornelius van Niel, who demonstrated that the oxygen liberated during photosynthesis originates from water molecules, not from carbon dioxide. His work with green and purple sulfur bacteria showed that when H₂S was used as a hydrogen donor instead of H₂O, sulfur or sulfate was produced instead of oxygen, indicating that water is the source of the oxygen released during photosynthesis.
In summary, the splitting of water molecules during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is the source of the oxygen released by plants, underscoring the pivotal role of photolysis in sustaining aerobic life on Earth.