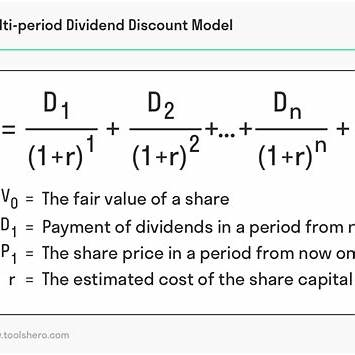
What assumption is required to derive the Dividend Discount Model (DDM)?
Task:
Identify the key assumption underlying the DDM.
Critically evaluate the validity of this assumption in real-world scenarios, considering factors such as:
Companies’ dividend policies.
Market dynamics and investor behavior.
Applicability across different industries.
The correct answer and explanation is :
Key Assumption of the Dividend Discount Model (DDM)
The fundamental assumption underlying the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) is that a company will continue to pay and grow its dividends indefinitely at a constant or predictable rate.
Critical Evaluation of This Assumption
1. Companies’ Dividend Policies
In reality, not all companies pay dividends consistently. Many growth-oriented firms, such as technology startups, prefer to reinvest profits rather than distribute them as dividends. Additionally, dividend policies can change due to financial distress, shifts in management strategy, or economic downturns. This makes the assumption of perpetual dividends problematic for many firms.
2. Market Dynamics and Investor Behavior
Market conditions influence dividend policies. During economic crises, companies may cut or suspend dividends, making future dividends unpredictable. Moreover, investor behavior is often driven by capital gains rather than dividends, especially in industries where stock appreciation outweighs dividend yield in importance. This contradicts the assumption that dividends are the primary determinant of a stock’s value.
3. Applicability Across Industries
The DDM is more applicable to mature, stable companies in industries such as utilities, consumer goods, and banking, where dividends are a significant component of shareholder returns. However, it is less useful for industries with high volatility, irregular earnings, or no dividend payments, such as technology and biotech. In such cases, alternative valuation methods like the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model or Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio are preferred.
Conclusion
While the DDM provides a straightforward valuation approach, its assumption of perpetual and predictable dividends limits its practical use. It is most effective for established dividend-paying companies but fails in valuing high-growth or non-dividend-paying firms.
Image