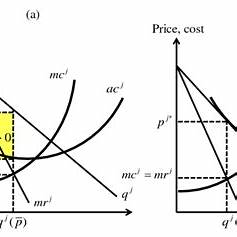
A monopolistically competitive firm in short runequilibrium:
Select correct option:
A Will make negative profit(lose money).
B Will make zero profit (break-even).
C Will make positive profit.
D Any of the given is possible.
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct option is:
D. Any of the given is possible.
Explanation:
In the short-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm, the firm can either make positive profit, negative profit, or zero profit. This is because monopolistically competitive markets have characteristics of both perfect competition and monopoly, which influence the firm’s ability to earn profits.
Here are the factors affecting the outcome:
- Positive Profit: If the firm’s price (P) is above its average total cost (ATC), the firm will earn positive profits. In the short run, if demand is strong and the firm can differentiate its product from competitors, it may be able to charge a price higher than its ATC, leading to profits.
- Negative Profit: If the price is below the average total cost, the firm will experience losses. Even in monopolistic competition, firms may experience losses in the short run if their costs are too high or if the market conditions (such as consumer preference or demand) are unfavorable. This can occur if the firm is in a period of declining demand or if its product differentiation is not enough to sustain higher prices.
- Zero Profit (Break-even): In monopolistic competition, firms will tend to break even in the long run because of the entry and exit of firms. However, in the short run, it is also possible for a firm to earn zero profit. This would happen if the price exactly equals the average total cost (P = ATC). In this scenario, the firm is covering all of its costs but is not making any extra profit.
The important takeaway is that in monopolistic competition, short-run profits or losses depend on where the firm’s price and cost structures align. There is no guarantee of zero profit or positive profit in the short run.
The equilibrium price and output are determined by the firm’s marginal cost (MC), marginal revenue (MR), and the positioning of the demand curve.
Image: