N B M V EXERCISE 7 REVIEW SHEET
Overview of the Skeleton
Lab Time: __________
Date: __________
Name: __________
Column B
condyle Bone Markings
- Match the terms in columns with the appropriate description in column A:
Column A
- sharp, slender process
- small rounded projection
- large rounded projection
- structure supported on neck
- armlike projection
- rounded, convex projection
- canal-like structure
- round or oval opening through a bone
- shallow depression
- air-filled cavity
- large, irregularly shaped projection
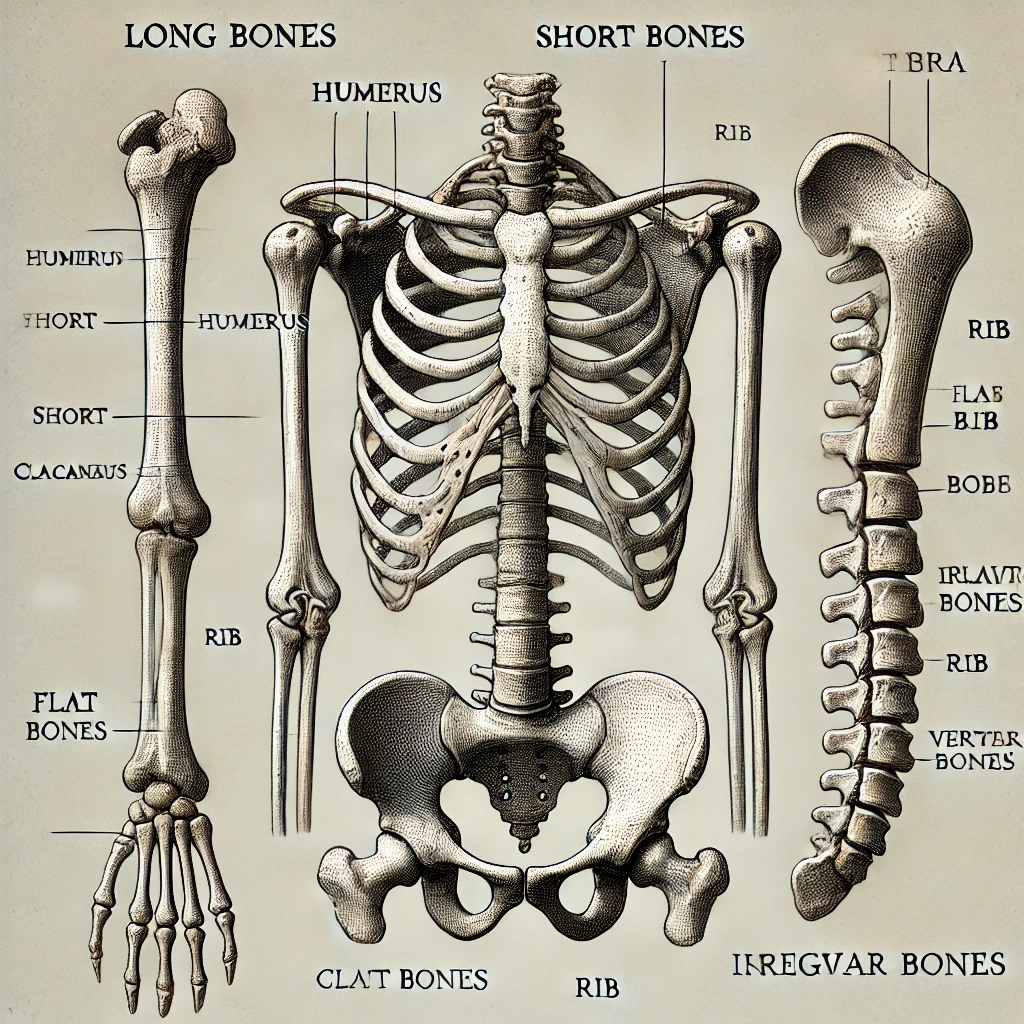
Classification of Bones
- The four major anatomical classifications of bones are long, short, flat, and irregular. Which category has the least amount of spongy bone relative to its total volume?
- Classify each of the bones in the following chart into one of the four major categories by checking the appropriate column. Use appropriate references as necessary.
| Long | Short | Flat | Irregular |
|---|---|---|---|
| Humerus | Phalanx | Parietal (skull bone) | Calcaneus (tarsal bone) |
| Rib | Vertebra |
The correct answer and explanation is:
Here’s your review sheet with answers and explanations:
N B M V EXERCISE 7 REVIEW SHEET
Overview of the Skeleton
Lab Time: __________
Date: __________
Name: __________
Bone Markings Matching
Match the terms in Column B with their appropriate description in Column A:
| Column A (Description) | Column B (Bone Marking) |
|---|---|
| sharp, slender process | Spine |
| small rounded projection | Tubercle |
| large rounded projection | Tuberosity |
| structure supported on neck | Head |
| armlike projection | Ramus |
| rounded, convex projection | Condyle |
| canal-like structure | Meatus |
| round or oval opening through a bone | Foramen |
| shallow depression | Fossa |
| air-filled cavity | Sinus |
| large, irregularly shaped projection | Trochanter |
Classification of Bones
The four major anatomical classifications of bones are long, short, flat, and irregular. The category with the least amount of spongy bone relative to its total volume is long bones because they primarily consist of compact bone with a medullary cavity containing bone marrow.
Bone Classification Chart
| Bone | Long | Short | Flat | Irregular |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humerus | ✅ | |||
| Phalanx | ✅ | |||
| Parietal (skull bone) | ✅ | |||
| Calcaneus (tarsal bone) | ✅ | |||
| Rib | ✅ | |||
| Vertebra | ✅ |
Explanation
The human skeleton is composed of 206 bones, which are categorized based on their shape and function. The four primary classifications of bones are long, short, flat, and irregular bones.
Long bones (e.g., humerus, phalanges) are characterized by their elongated shape and consist mostly of compact bone. These bones provide structural support, leverage, and movement, making them essential in locomotion. They have a diaphysis (shaft), epiphyses (ends), and a medullary cavity containing bone marrow.
Short bones (e.g., calcaneus) are cube-shaped and mostly composed of spongy bone with a thin outer layer of compact bone. They provide stability and support with minimal movement, commonly found in areas like the wrist (carpals) and ankle (tarsals).
Flat bones (e.g., ribs, parietal bone) are thin, flattened, and usually slightly curved. These bones are designed for protection and serve as sites for muscle attachment. Their composition includes two layers of compact bone sandwiching a layer of spongy bone, providing strength while remaining lightweight.
Irregular bones (e.g., vertebrae) have complex shapes that do not fit into other categories. They have a mix of compact and spongy bone, contributing to protection (e.g., vertebrae protect the spinal cord) and support for the body.
Each bone marking serves a functional role, from providing attachment sites for muscles to forming passageways for nerves and blood vessels. Understanding the skeletal structure is crucial for fields like medicine, sports science, and physical therapy.
Generated Image
I’ll create an image illustrating the four major bone classifications.
Here is the anatomical diagram illustrating the four major classifications of bones. Let me know if you need any modifications or further explanations!