What process authenticates clients to a network?
Four-way handshake
TKIP
WPA2
HMAC-SHA
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct answer to the question is Four-way handshake.
Explanation:
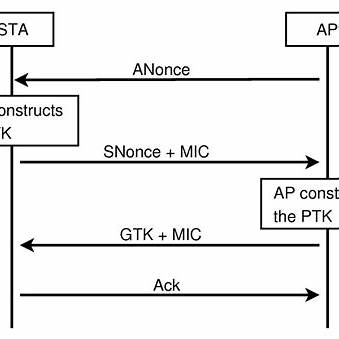
The Four-way handshake is the process that authenticates clients to a wireless network, specifically in Wi-Fi security protocols such as WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2). It is designed to securely establish a connection between the client (like a laptop or smartphone) and the access point (AP), ensuring that both parties are authorized to communicate, and that the data exchanged is encrypted.
Here’s a breakdown of the Four-way handshake process:
- Step 1 – AP to Client (Message 1):
- The access point (AP) sends a nonce (random number) to the client. This nonce is a one-time number used to generate encryption keys.
- Step 2 – Client to AP (Message 2):
- The client responds with its own nonce and a MIC (Message Integrity Code) to verify that it knows the pre-shared key (PSK) without sending the key itself. The client also derives a unique session key from the PSK and the nonces.
- Step 3 – AP to Client (Message 3):
- The AP acknowledges the client’s response and sends its own confirmation message, including a session key for encryption. This key is shared between the client and AP.
- Step 4 – Client to AP (Message 4):
- The client sends a confirmation message back to the AP, completing the handshake. The connection is now secure, and the session encryption keys are active, allowing data communication to occur safely.
This process is essential because it ensures mutual authentication between the client and the AP without exposing the actual password. It also facilitates the creation of fresh encryption keys for every session, which protects against various types of attacks.
Other terms:
- TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) is an older encryption protocol used in WPA (but not WPA2). It’s vulnerable and not as secure as WPA2.
- WPA2 refers to a Wi-Fi security standard that uses AES encryption and is more secure than WPA.
- HMAC-SHA1 (Hashed Message Authentication Code using SHA-1) is a cryptographic algorithm used to verify the integrity and authenticity of a message but is not specifically the process used for authenticating clients to a network.
Image: