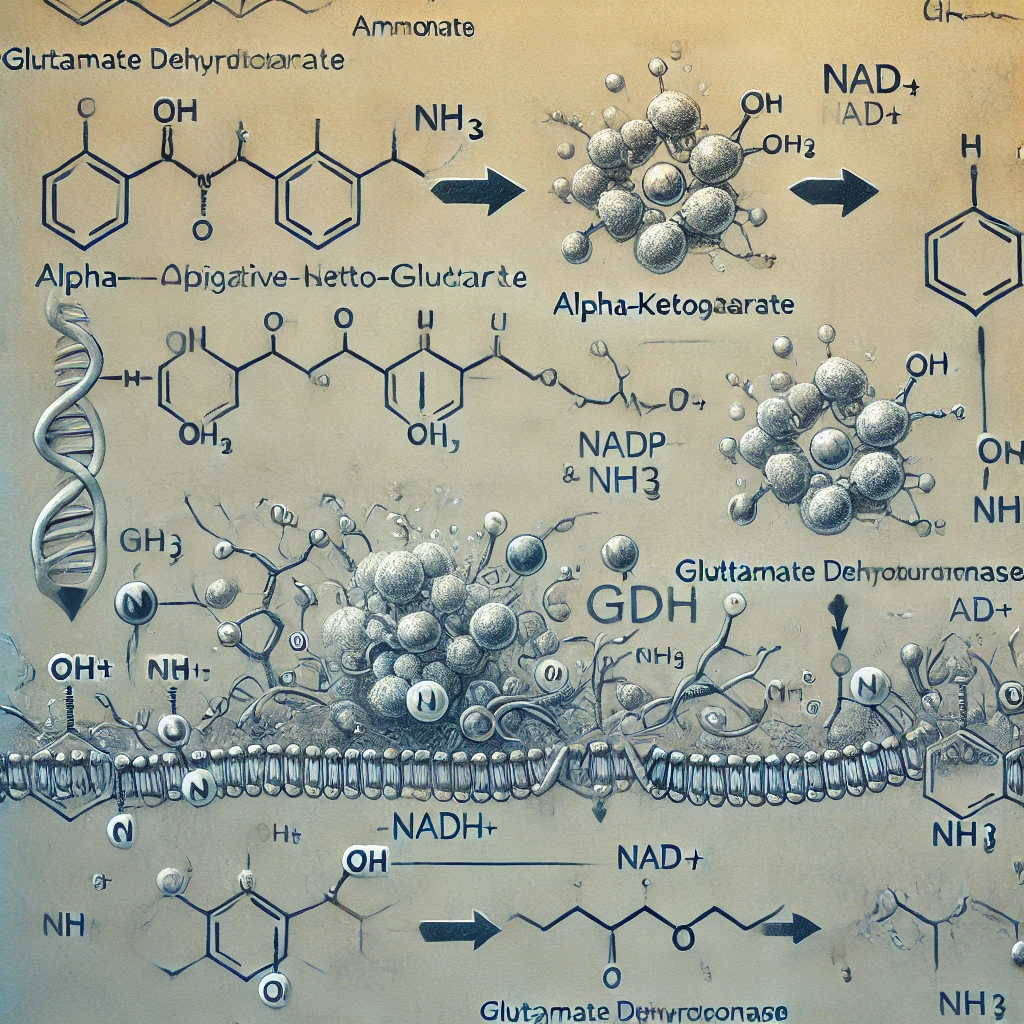
In the oxidative deamination of glutamate, alpha-ketoglutarate is one of the products.
a.All three statements are true.
b.Two of the three statements are true.
c.Only one of the statements is true.
d.None of the statements is true.
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct answer is:
a. All three statements are true.
Explanation:
Oxidative deamination is a biochemical reaction that involves the removal of an amino group from an amino acid, resulting in the formation of a corresponding keto acid and ammonia (NH₃). In this process, glutamate undergoes oxidative deamination to produce alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia, catalyzed by the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase. This reaction occurs mainly in the liver and is essential for nitrogen metabolism.
Reaction Mechanism:
- Substrate: The reaction begins with glutamate.
- Enzyme: Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) catalyzes the reaction.
- Cofactors: Either NAD+ or NADP+ serves as an electron acceptor.
- Products: The oxidation of glutamate leads to the formation of alpha-ketoglutarate, a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and ammonia (NH₃), which later enters the urea cycle for detoxification.
Importance of Oxidative Deamination of Glutamate:
- Nitrogen Metabolism: Ammonia is a toxic byproduct, so its removal via the urea cycle is crucial.
- Energy Production: Alpha-ketoglutarate enters the citric acid cycle, contributing to ATP generation.
- Amino Acid Catabolism: This process is central to breaking down amino acids for energy or biosynthesis.
Since the statement provided correctly identifies alpha-ketoglutarate as a product of oxidative deamination of glutamate, and there are no false statements present, the correct answer is option (a) – all three statements are true.