Free energy is often given in units of kJ/mol or kcal/mol. One kilocalorie is equal to 4,186.8 joules. A particular reaction has a standard free energy change of -30.5 kJ/mol. What is the standard free energy change in units of kcal/mol? (Give your answer as a numeral only with one decimal place.)
The correct answer and explanation is :
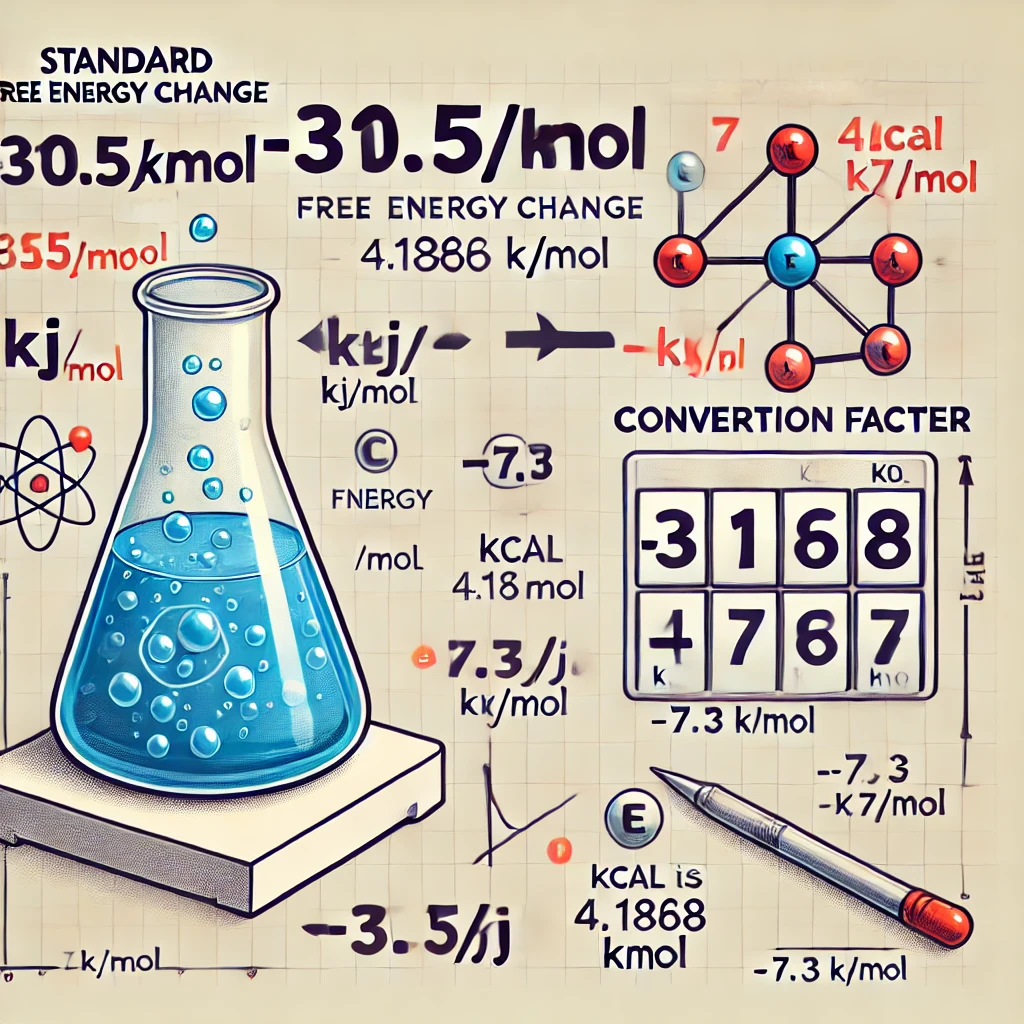
The correct answer is: -7.3
Here’s a detailed explanation:
In thermodynamics, the standard free energy change (ΔG°) is often expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). These units are used to describe the amount of energy associated with chemical reactions, especially whether the reaction releases or absorbs energy under standard conditions.
In this problem, we’re given a standard free energy change of -30.5 kJ/mol and asked to convert this to kcal/mol. To do this, we use the conversion factor:
1 kilocalorie (kcal) = 4.1868 kilojoules (kJ)
To convert kilojoules to kilocalories, divide the number of kilojoules by the conversion factor:
[
\frac{-30.5 \text{ kJ/mol}}{4.1868 \text{ kJ/kcal}} \approx -7.3 \text{ kcal/mol}
]
This means the reaction releases 7.3 kilocalories of energy per mole of substance under standard conditions. The negative sign indicates that this is an exergonic reaction — energy is released, making the process spontaneous under standard conditions.
Understanding the unit conversion is crucial in scientific disciplines, especially biochemistry, where ATP hydrolysis (a key energy-releasing reaction in cells) has a standard free energy change of approximately -30.5 kJ/mol — just like in this problem. Converting this to kcal/mol helps scientists interpret energy changes in units more commonly used in nutrition and biology.